The Role of AI in Automotive Battery-Management Systems
What you’ll learn:
- The core challenges with traditional EV BMS architectures.
- Types of AI applied in the automotive industry.
- How AI optimizes state of charge, state of health, and range prediction in an EV BMS.
- Real-world examples from Electra Vehicles and Texas Instruments.
In the world of electric vehicles (EVs), where range anxiety and battery longevity are primary concerns of consumers, a silent revolution might be underway: Artificial intelligence (AI) is making its way into the center of EV technology—the battery-management system (BMS). While AI often gets more attention than it deserves in nearly any industry, the question is “why and how is AI applied in the context of automotive batteries, and can it enable a precise EV range prediction over the entire vehicle’s lifetime?”
EV Batteries: A Playground for AI
When it comes to AI's insatiable appetite for complex problems and large datasets, EV batteries offer the perfect playground. A lithium-ion battery pack, comprised of hundreds or even thousands of individual "breathing" electrochemical cells (Fig. 1), reacts with extreme sensitivity. Such sensitivity doesn’t just involve slight deviations and impurities during manufacturing, though. It also reacts to real-world conditions once installed in an EV—electrical variations during charging and driving, environmental factors, and often-overlooked mechanical pressure and vibrations.
As batteries charge/discharge and age, they literally “breathe” and swell. This leads to volume changes that can reach up to about 15% in the case of some all-solid-state battery chemistries.
These influences from manufacturing and operations manifest in the vehicle as battery capacity (range) and power loss over time—a phenomenon both critically important for end-users and, paradoxically, frustratingly opaque to the industry.
On a microscopic scale, this complexity boils down to lithium-ion intercalation processes in the anode and cathode of each individual cell, the formation of solid-electrolyte-interphase (SEI) layers, and in ionic diffusion pathways. At the battery-pack level, the only accessible signals in commercialized EVs are nothing more than the pack current, cell voltages, and a few temperature sensors.
Bridging this gap to map all relevant phenomena and correlations is a challenge being tackled from two directions: physics-based electrochemical modeling at the sub-cell level and big-data-driven machine-learning algorithms at the vehicle fleet level. With complex correlations and vast datasets emerging from lab tests and real-world vehicles, the question arises: “Is there untapped potential for AI?”
>>Check out this TechXchange for similar articles and videos
The Role of the Automotive BMS
If battery chemistry is the heart of an EV, the battery-management system is its brain. It manages the behavior of individual battery cells, their interaction with the drivetrain, and their response to charging systems.
With the diversity of EV battery designs, cell formats, and chemistries, a one-size-fits-all BMS doesn’t exist. Each system is tailored to the specific battery architecture, comprising hardware and software elements like battery-monitoring units, high-voltage disconnectors, isolation monitors, and pyro fuses.
An automotive BMS’s primary functions include:
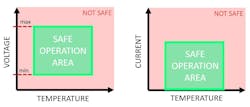
Safety monitoring: The BMS continuously monitors battery temperature, voltage, and current to prevent dangerous/damaging conditions like overcharging/discharging or overheating (Fig. 2).
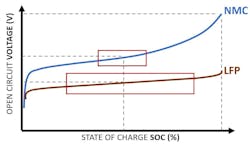
State estimation: Perhaps the most crucial and challenging task of a BMS is accurately estimating the battery's state of charge (SOC)—the measure of how much energy is currently available in the battery—and state of health (SOH), which reflects the overall condition and capacity of the aged battery compared to its original state (Fig. 3). The latter is inherently important when assessing the resale value of an EV as about 30% of an EV’s net cost is its battery.
Cell balancing: To maximize battery life and performance, the BMS ensures that all cells in the battery pack are charged and discharged uniformly.
Thermal management: The BMS controls cooling systems to maintain optimal battery temperature, crucial for performance and longevity.
Data communication: The BMS interfaces with other vehicle systems, providing critical battery information to the driver and other control units.
One promising area where AI is having a significant impact is in state estimation. Paradoxically, the most talked-about quantity in an EV—its range—isn’t a directly measured value; it’s an estimation. Historically, state estimation has relied on pre-defined algorithms and lookup tables developed through extensive lab testing. But is this traditional approach enough in a world where real-world driving conditions and battery aging introduce unending variability?
Where Traditional BMS Approaches Fall Short
Developing a BMS is a resource-intensive task, deeply tied to the unique architecture of each battery pack. The most expensive and time-consuming part is the calibration of the BMS as it relies on extensive lab testing of the battery at hand.
Cells, modules, and packs undergo years of rigorous testing under varied conditions to map their electrochemical behavior. These tests encompass performance assessments, safety evaluations, and lifetime measurements. The data collected forms the foundation for battery models and for static lookup tables, which serve as the backbone of traditional BMS algorithms.
Thus, these lookup tables can be seen as pre-computed datasets that map parameters like the open circuit voltage (OCV) of the battery to actual SOC across different temperatures, typically from −20 to 60°C. Additional dimensions, such SOH and charge/discharge rates (C-rates), are often incorporated for greater precision.
To process these tables and use them in an actual vehicle, traditional BMS algorithms rely on parametrized battery models combined with techniques such as Kalman filters and their variants. Kalman filters dynamically integrate data on voltage, current, and temperature to estimate the SOC and SOH. They rely on highly accurate cell voltage measurements, especially in batteries with lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) cathode chemistry that exhibits flat voltage profiles, making small measurement deviations lead to significant prediction errors (Fig. 4).
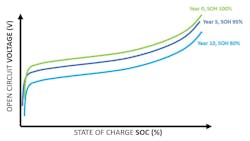
These methods are constrained by static models and prone to cumulative errors, particularly as batteries age (Fig. 5), or operate under atypical conditions. This is where AI unlocks dynamic, data-driven solutions.
AI’s Opportunity in EV BMS Systems
These limitations of traditional BMS methodologies highlight the need for smarter, more adaptive systems. AI brings opportunities to three key areas of application:
1. Improving accuracy of SOC and SOH estimation
One of the central reasons for using AI in BMS state estimation lies precisely in harnessing the dynamic nature of real-world driving conditions and battery-aging processes. This is achieved by leveraging the vast amounts of battery data through machine learning at the edge—"edge computing.”
Instead of the previously mentioned static lookup tables created in laboratory environments, complex neural networks are directly embedded into vehicle chips. These networks continuously learn how the battery is utilized by specific drivers in their unique environments.
This enables adaptive BMS systems, which incorporate recalibration steps to eventually evolve into intelligent systems capable of self-learning and collaboration across fleets by using cloud connectivity.
An example of this is Electra Vehicles, who uses neural-network-based algorithms to analyze data from the battery, vehicle, driver, and environment. These algorithms, deployed at the edge on microprocessors such as those from Texas Instruments, enable real-time adjustments and continuous improvements (see video below). Recent results demonstrate that this approach achieves remarkable precision—less than 1% error in SOC estimation and under 3% in SOH—significantly enhancing range prediction accuracy over the battery’s lifetime.
2. Improving safety and predictive maintenance
It’s encouraging to know that the next charging station can be reached with 99% confidence. However, a second area where AI can create incredible value for an EV BMS is in the safety system and in predictive maintenance. Machine learning can identify patterns and train itself to detect, based on specific variations in temperature, voltage, and current, whether a battery may have a safety issue or require repair.
Knowing exactly how long the battery can still be used and how many cycles it can complete before requiring maintenance is particularly useful to commercial fleet operators. While definitive proof of this capability is still lacking, despite many companies claiming to achieve it, the potential is undeniably there.
3. AI can be applied to reduce cell testing and BMS development time
A final area that has become relevant moves away from the actual vehicle operations and applies AI during the development phase. Even though AI is transforming BMS systems into self-learning systems, the technology isn’t yet at the point where it can completely eliminate the need for battery lab testing.
But with the right collaborations across the ecosystem, AI can be applied in this area to significantly reduce the required tests. This goes beyond the currently predominant, statistics-driven design of experiments. For example, Monolith has demonstrated how AI can reduce the need for aging tests by 40% and cell repetitions by 75%.
Summary and Outlook: AI’s Future in EV Battery Development and Management
Artificial intelligence is redefining the way electric-vehicle batteries are managed, improving accuracy, safety, and efficiency across the lifecycle of a battery. However, skepticism around AI remains—and rightly so. While many promises are being made, tangible proof of AI's full potential in certain areas, such as long-term predictive maintenance, is still emerging, with predictions of failure up to three months in advance. Nonetheless, the transformative potential of AI can’t be ignored.
References
Dr. Veronika Wright, "What Is a Battery Management System (BMS)?"
Dr. Veronika Wright, “Artificial Intelligence in the E-Mobility Industry.”
Electra Vehicles and Texas Instruments Podcast Episode, "AI in E-Mobility Series."
>>Check out this TechXchange for similar articles and videos
About the Author
Dr. Veronika Wright
CEO, Electrified Veronika
Veronika Wright earned her PhD in Technical Physics from Graz University of Technology in Austria. Her career in the automotive industry began at AVL List GmbH, where she developed expertise in batteries, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. In 2021, she established her consulting practice, providing technical and strategic guidance, educational support, mentoring, and expert advice in battery technology and clean transportation.
In 2025, Veronika launched a new venture, Electrification Academy, a B2B knowledge platform designed to provides insights into innovative solutions across battery development, manufacturing, and recycling. Author of The Drive to Electric: How Innovative Minds Are Shaping Our Future, Veronika drives conversations on the future of mobility.