Active Antialias Filter for 24-bit ADC Features Low Distortion, High SNR (.PDF Download)
For many analog-to-digital converter (ADC) applications, a simple passive resistor/capacitor (RC) filter at the buffer input will provide adequate antialiasing filtering. However, an active filter is often needed for higher-resolution, low-noise applications that require higher-order filtering. The active component in that filter must have sufficient bandwidth, fast settling time, low noise, and low offset voltage so that it doesn’t corrupt the signal before it gets to the ADC.
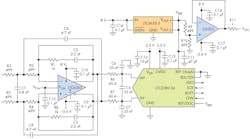
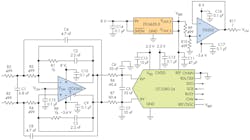
This circuit uses a differential op amp optimized to drive a low-power successive-approximation-register (SAR) ADC, although it will work for other converters as well (Fig. 1). It provides a 30-kHz, third-order filter based on op amp U2 (LTC6363), which has 500-MHz gain-bandwidth product, 780-ns settling time to 4-ppm, 2.9-nV/√Hz input-referred noise, and a maximum offset voltage of 100 µV. U2 is optimized to drive U1 (LTC2380-24), a 1.5/2-Msample/s, low-power SAR ADC with an integrated digital filter that can average from 1 to 65,536 conversion results in real time, thus providing an increase in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
1. The 30-kHz, third-order active filter centered on op amp U2 drives the 24-bit ADC with the necessary bandwidth, fast settling time, low noise level, and low offset voltage.