Domestic Digitalization: Wireless in Home Appliances (Part 1) (.PDF Download)
Many smart appliances are anything but smart. They use connectivity in a limited way to simply control appliances remotely. But the Internet of Things (IoT) enables us to implement much greater functionality than this.
Today’s consumer has a sophisticated perception of what living in a connected world means, and smart internet services have become far more mature than what was offered in first-generation connected white goods. Consumer expectations present an interesting challenge to the manufacturers and retailers of smart-home appliances, pushing them to innovate new capabilities and services.
All major appliance makers are gearing up to embrace the challenge and bring next-gen domestic digitalization to market. Internet and connectivity are no longer just add-on features; they are now at the very core of product positioning and brand extension to bundled services people hadn’t even imagined a few years back.
What Smart Services Can You Expect?
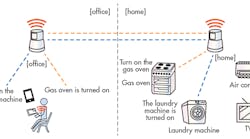
Controlling remotely: Cloud connectivity makes it possible to control appliances from outside of your residence. One example is the ability to review a real-time feed about room temperature in your house and switch on the air conditioner when you leave the office. Figure 1 shows another example of remote control.
1. Wireless remote control is enabled with a smartphone via Wi-Fi and the internet.
Intelligent assistance: Smart devices can have a say in how households are run by offering useful tips and helping consumers make informed decisions. For example, a connected refrigerator with freshness detection sensors inside its special compartments could indicate the freshness of the raw items stored in them. Using a relative freshness index and expected shelf-life of product, it could further guide users as to which items to use first. The fridge could also map food-to-use with recipes from partner websites and offer suggestions as to what to cook for dinner.
Ecosystem interoperability: An intranet of connected appliances together can form a cohesive ecosystem to build synergies between the appliances. For instance, once a user has chosen a recipe from the list suggested by the refrigerator, the refrigerator could notify the oven to set itself to the appropriate preheating conditions based on what’s about to be cooked.