The term omni-robotics is very seldom used as part of our terminology speech. We have a tendency to classify our robots by manufacturer and number of axes, or more appropriately, degrees of freedom (DoF). Some of us still define a robot by the early concept—a robot is a machine that handles the three Ds: Dull, Dirty, and Dangerous.
The word omni is defined as “all.” This could lead to, perhaps, referring to all 6-axis arms as “omni-arms.” What this means is that all of the arms have the same type of motion and the same basic function: to move the end-effector from point A to B.
All 6-axis robots from Kuka, ABB, or Yaskawa Motoman have the same basic function. What makes them unique is the end-effector or payload. Generally, an entire factory doesn’t have the same robot model throughout. We then differentiate its job by the end-effector and the software to control it. This article will look more at the basic hardware than the complex software used to create a full functioning robot.
The omni-robotics term is not really used in the robotic arm industry. I began using it for a new type of robot called the “Omni-chassis.” This is a powered robotic chassis that can carry different payloads or functioning modules. The Omni-chassis covered in this article comes as a 6-wheel or track version. We usually explain this concept as akin to buying a garden tractor and adding the attachments you need for your yard/project. The attachments are normally called payloads because they mount onto the chassis.
Omni-chassis Sections
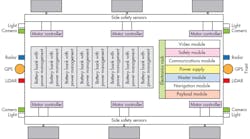
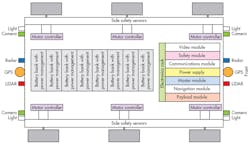
This article breaks down into explanations of the various sections of the chassis. Figure 1 is basic diagram for a 6-wheel Omni-chassis.
1. The 6-wheel Omni-chassis has individual motors for each wheel, and is surrounded by an array of sensors.