What’s the Difference Between Ethernet and Time-Sensitive Networking? (.PDF Download)
These days, anyone working in industrial communications is bound to come up against the topic of time-sensitive networking (TSN). TSN will definitely get here. The only thing that still must be clarified is when and in what form. However, even today, the its advantages for industrial communications aren’t always clear.
History
Ethernet was introduced to offices in the early 1980s and quickly became very popular due to its high throughput of (at that time) a sensational 10 Mb/s. However, this Ethernet wasn’t practical for real-time applications because it used a common medium known as a party line. Collisions occurring at high utilization rates caused problems in office settings.
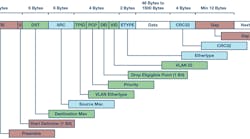
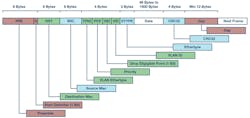
1. In this Ethernet frame, data fields relevant to TSN data-flow identification are shown in green.
In the next step of its development, collisions were eliminated through the introduction of switched networks. In addition, with quality of service (QoS), Ethernet datagram prioritization was introduced (Fig. 1).
For industrial applications, guaranteed latency is particularly important. Despite QoS, standard Ethernet as used in offices can only guarantee latencies up to a certain point, especially with high network utilization.