AMD’s Ryzen processor (Fig. 1) incorporates a wide range of improvements, including artificial intelligence for its branch prediction. The 8-core chip implements simultaneous multithreading supporting 16 threads (8C/16T). It has a TDP under 100 w and is delivering performance similar or better than Intel’s Core i7-6900K that has a 140 W TDP. Some of the chip’s details are sketchy, but it clock starts at 3.4 GHz.
AMD employs a neural network in its branch prediction subsystem. It builds a model of the code being executed so that its Smart Prefetch can pre-load instructions and optimize the path through the processor pipeline. The neural network is designed to learn from the currently running applications rather than the predefined static analysis often used in other deep learning applications.
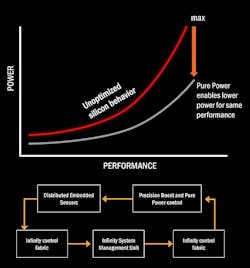
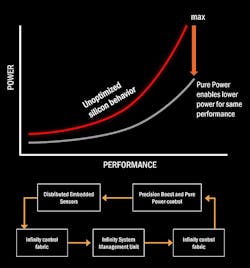
AMD’s Pure Power technology (Fig. 2) is designed to minimize power requirements while providing optimum performance. The “infinity fabric” is a power management system that works throughout the chip to monitor and control the temperature, clock frequency, and system voltages. The Infinity System Management Unit provides the adjustments.
The Ryzen SenseMI (pronounced “Sense Em-Eye”) technology implements automatic overclocking. The system also improves cooling when combined with the Pure Power support and the Precision Boost uses a 25 MHz granularity. The Extended Frequency Range (XFR) is designed for overclockers that have high-end cooling systems.
The chip will run on AMD’s AM4 motherboard with the Bristol Ridge chipset. It has a dual memory channel DDR4 memory subsystem. It supports USB 3.1 Gen 2, NVMe, and SATA Express.
Ryzen represents a significant performance boost that puts it on par with the fastest Intel desktop chips while utilizing less power. The anticipated price for Ryzen is less than Intel’s Intel Core i7 6900K that has a street price around $1,000, and it should bring some price competition in the high-end gaming space in 2017.
About the Author
William G. Wong
Senior Content Director - Electronic Design and Microwaves & RF
I am Editor of Electronic Design focusing on embedded, software, and systems. As Senior Content Director, I also manage Microwaves & RF and I work with a great team of editors to provide engineers, programmers, developers and technical managers with interesting and useful articles and videos on a regular basis. Check out our free newsletters to see the latest content.
You can send press releases for new products for possible coverage on the website. I am also interested in receiving contributed articles for publishing on our website. Use our template and send to me along with a signed release form.
Check out my blog, AltEmbedded on Electronic Design, as well as his latest articles on this site that are listed below.
You can visit my social media via these links:
- AltEmbedded on Electronic Design
- Bill Wong on Facebook
- @AltEmbedded on Twitter
- Bill Wong on LinkedIn
I earned a Bachelor of Electrical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and a Masters in Computer Science from Rutgers University. I still do a bit of programming using everything from C and C++ to Rust and Ada/SPARK. I do a bit of PHP programming for Drupal websites. I have posted a few Drupal modules.
I still get a hand on software and electronic hardware. Some of this can be found on our Kit Close-Up video series. You can also see me on many of our TechXchange Talk videos. I am interested in a range of projects from robotics to artificial intelligence.