Electromagnetic Induction: The Basic Principle Behind Wireless Power
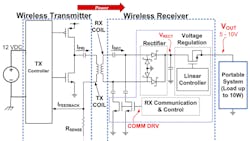
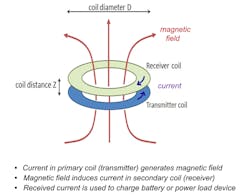
A basic concept of wireless power is shown in Figure 1. Simple low-power wireless-charging systems such as electric toothbrushes often operate in an “open-loop” configuration and may not be well regulated at the receiver output. The charging source simply generates a continuous ac excitation on the primary coil. When the portable device is placed on it, power is applied to the load to charge the internal battery.
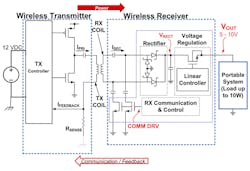
An open-loop unregulated system may be acceptable for low output-power levels of, say, less than 1 W. However, at higher power levels, it becomes both wasteful and inefficient, generating lots of heat. Unlike the open-loop approach used in simple wireless-power applications, an intelligent wireless-power system has microcontrollers on both receive (RX) and transmit (TX) side circuits (Fig. 2).
The transmitter doesn’t generate output power unless it knows that a valid receiver is placed on it. Therefore, if a transmit pad is plugged in with nothing sitting on it, very little power is wasted.
When placing a valid (recognized) device on the charging pad (or table), the transmitter only delivers the level of output required, as requested by the receive controller based on the needed load-current level. Feedback is provided from the receiver back to the transmitter back through the same inductive coupling as the forward power transfer (“in-band” communication). Alternatively, it may be in the form of a dedicated separate communication link such as Bluetooth (“out-of-band” communication).
For a more detailed introduction to the basic concepts of wireless power, see reference 1. References 2-7 provide additional system design guidelines for wireless-power implementations.
References:
- Sengupta & Johns, “Universally compatible wireless power using the Qi protocol,” Low-Power Design, October 1, 2011
- Tahar Allag, “Test and troubleshoot a wireless power receiver,” Application Report (SLUA724), August 2014 Instruments
- Johns, Antonacci, and Siddabatula, “Designing a Qi-compliant receiver coil for wireless power systems,” Analog Applications Journal (SLYT479), 3Q 2012
- Tahar Allag, “Layout Guidelines for wireless power receiver,” Application Report (SLUA710), June 2014
- Ilya Kovarik, “Building a wireless power transmitter,” Application Report (SLUA635A), August 2012
- Jing Ye, “NVDC charging design considerations,” Video Tutorial.
- Norelis Medina, 10W Wireless power system lab demo, Video
About the Author
Upal Sengupta
Applications Manager, Battery Management Solutions
Upal Sengupta is an applications manager with the Texas Instruments Battery Management Solutions group. He received a BSEE from the University of Illinois, and an MSEE from Michigan State University.
Dick Stacey
Applications Engineer, Wireless and Low Power Charging
Dick Stacey, an applications engineer in the Wireless and Low Power Charging team at Texas Instruments, has previously held roles in systems engineering, test engineering, and marketing for power-management products. He received his BSEE from the University of Texas at Austin.
Bill Johns
Applications Engineer, Wireless Power
Bill Johns, an applications engineer for Wireless Power at Texas Instruments, specializes in power conversion for portable battery-powered applications. He received his BSEE from University of Texas in Dallas.