Small Lead “Twist” Makes Safety Resistors Surface-Mount Compatible
What you’ll learn:
- How a small change in lead arrangement transforms a through-hole component into a surface-mount version.
- The role of safety resistors in power-meter, appliance, and automotive applications.
- Why these resistors differ from conventional current-limiting resistors.
Despite the nearly total shift of the component and production world to surface-mount technology (SMT) and devices (SMD) whenever possible, some components are still offered only in leaded, through-hole packages. This may be due to one or more factors associated with these components: mechanical realities, thermal and mounting considerations, size and weight, regulatory mandates, or safety issues.
However, whenever possible, fabrication facilities that actually load and solder PCBs would prefer SMT devices due to their faster setup, integration, and compatibility with the production flow.
Vishay’s Wirewound Safety Resistors with WSZ Lead Form
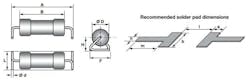
Addressing the preference for SMDs, Vishay Intertechnology announced that its AC03-CS series of axial, cemented, leaded, wirewound safety resistors is now available with a pick-and-place-friendly lead-bending option dubbed the WSZ lead form, which allows them to be used as surface-mount components (Fig. 1). The “twist” bridges the apparent contradiction of having leads while being surface-mount compatible.
These safety resistors, also known as fusible resistors, are a type of resistor that functions as both a current-limiting resistor and a fuse. It allows for normal current flow under standard operating conditions. However, it will break the circuit if the current exceeds a safe level, preventing damage to other components.
As with so many so-called “simple” components, there’s more to these resistors than meets the eye. For example, their specially developed silicone-lacquer coating has superior thermal and electrical insulating properties. Thus, designers can more easily meet the requirements for safety approval, while eliminating the need to put additional fuses in series with the input resistor. Note that their “twisted lead” requires T-shaped PCB pads, but that’s a minor inconvenience in exchange for the SMD attribute (Fig. 2).
The devices ensure safe and silent fusing when high DC-voltage overload or accidental AC-mains voltage of 120/240 V RMS is applied. At the same time, their silicone-cement coating allows the devices to safeguard the PCB and other components by minimizing the risk of fire due to extreme electrical overloads. And it does so without the need for additional fuses in series.
Applications for These Resistors
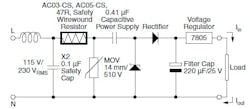
A typical application is the capacitive-based power supply (often called a “cap-drop” topology and only sensible and viable for well-controlled loads) in a single-phase energy meter (Fig. 3). Whenever the metal-oxide varistor (MOV) is short-circuited due to repetitive action of a surge, the safety resistor handles the entire mains voltage across itself and limits in-rush current.
The resistor value is so chosen that it doesn’t dissipate too much power, yet it’s large enough to limit inrush current. The current through it is full-wave current equivalent to line voltage divided by impedance of the line capacitor. The AC03-CS series resistors are available with values from 1 to 100 Ω (±5 % tolerance) and a 3-W rating. They operate over a wide temperature range of −40 to +200°C with a TCR of 200 ppm/K.
In addition to their use in consumer products such as energy meters and appliances, they’re also AEC-Q200 qualified for automotive use. Their product page provides basic details with links to a datasheet and many other relevant documents.
References
“Silent Fusing” of AC-CS Safety Wirewound Resistors
Application of Leaded Resistors in Energy Meters
Application of AC03-CS, AC05-CS (UL 1412 Recognized)
AC03-CS Series Axial Cemented, Leaded Wirewound Safety Resistors Now Available