This article is part of the TechXchange: RISC-V: The Instruction-Set Alternative
What you’ll learn
- How RISC-V fits into motor-control tasks.
- What types of tools are available for development?
RISC-V is a topic that garners lots of interest, but RISC-V itself is nothing more than a scalable, open-source instruction set definition. It’s the implementation that makes things interesting. Though custom ASICs have been the realm for RISC-V implementations, now more application-specific standard parts (ASSP) are showing up. FPGAs that incorporated RISC-V were the first to emerge, but RISC-V ASSP solutions are becoming more generally available.
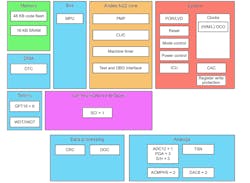
One example is Renesas’ R9A02G020 motor-control chip that can handle three-phase motors (see figure). The core is an Andes Technology N22 RV32I. This 32-bit integer microcontroller uses the AndeStar RISC-V-compliant V5/V5e instruction set. Leveraging a two-stage pipeline with a mixed 16/32-bit instruction format, it supports branch prediction and hardware multiply/divide. Its StackSafe hardware can be used to measure stack size to detect runtime stack overflow and underflow problems.
The process runs at 32 MHz and includes the Andes Physical Memory Protection unit (Andes PMP). On-chip memory consists of 48 kB of flash and 16 kB of SRAM. Each chip has a unique 128-bit identifier. The core-local interrupt controller (CLIC) provides interrupt management.
A clock frequency accuracy measurement circuit (CAC) can be used to generate an interrupt a reference count that’s not within range, which is handy for deterministic applications like motor control. There’s also register protection support, allowing the system to limit application access to certain registers.
Analog support includes a 12-bit ADC and dual 8-bit DACs. Also in the mix are a high-speed comparator and built-in temperature sensor. The system is designed to handle sensor-less vector control for one BLDC motor, 1/3 shunt, power factor correction (PFC), and Hall sensor inputs.
The data-processing block features hardware CRC support. The data operation circuit (DOC) is a digital comparator that compares, adds, and subtracts 16-bit data with the ability to generate an interrupt upon detection of a programmable condition.
The chips come in 24- and 32-pin QFN packages. They support temperatures up to 125°C, suiting them for harsh operating environments.
Renesas can deliver pre-programmed chips that have specialized application code developed by leading independent design houses (IDHs) BFG Engineering and DigiPower (HK) Technology Ltd. These companies specialize in motor-control software.
Developers also can take advantage of SEGGER Microcontroller’s software ecosystem. This includes the company’s Embedded Studio and J-Link that works with the chip’s JTAG interface.
Read more articles in the TechXchange: RISC-V: The Instruction-Set Alternative