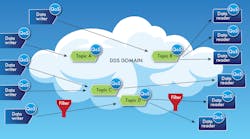
The Object Management Group’s (OMG) Data Distribution Service (DDS) is a middleware standard for data-centric connectivity (Fig. 1). DSS can provide a secure and robust publish/subscribe environment that allows applications to be written without dealing with connection details. DDS is available from a number of vendors, and there’s a range of open-source implementations as well.
1. The Object Management Group’s (OMG) Data Distribution Service (DDS), a middleware standard for data centric connectivity, uses a publish/subscribe model.
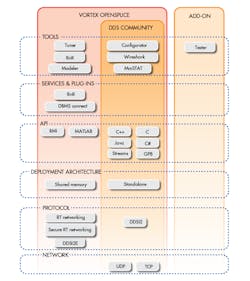
ADLINK Technology is the latest to provide part of its DDS implementation in the form of an open-source project (Fig. 2). The v6.7 community edition of the Prismtech Vortex OpenSplice platform is a subset of the commercial edition that adds protocols like Secure RT Networking and implements a shared-memory architecture that can handle more ambitious projects. It also offers more advanced tuning and configuration tools.
The community edition is now referred to as the Eclipse Cyclone project. This open-source ecosystem falls under the auspices of the Eclipse Foundation.
The community edition includes full support for TRANSIENT_LOCAL durability, so that each standalone “single-process” application doesn’t have to include a full durability-service (DS). ADLINK introduced the concept of “client-side durability,” where standalone “single-process” applications will transparently obtain historical (TRANSIENT and/or PERSISTENT) data from dynamically discovered durability services.
The latest edition supports ISOCPP and JAVA5 DCPS language bindings. It’s also compatible with the Future Airborne Capability Environment (FACE) 2.1 Transport Services Segment (TSS). On top of that, it supports the Google Protocol Buffers (GPB) as an alternative to the OMG-IDL definition for topic-types.
2. ADLINK’s DDS community edition is a subset of its commercial Vortex OpenSplice implementation.
“DDS has been witnessing incredible growth in adoption across a large number of application domains, culminating in its recommendation as part of virtually all Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Reference Architectures,” says Angelo Corsaro, CTO, PrismTech/ADLINK Technology. “With DDS Community Edition v6.7, we are making available the most advanced DDS implementation on the market under the liberal open source license—Apache license version 2.0. This will help reduce the IoT adoption barriers and further accelerate the penetration of DDS in this new and exciting market.”
Other open-source implementations of DDS with matching commercial support are available from Real-Time Innovations (RTI) with its Connext DDS. The OpenDDS project is supported by Object Computing, which also has a commercial version of DDS.
A number of commercial DDS implementations are available, including Kongsberg Geospatial’s InterCOM DDS, Twin Oaks Computing CoreDX DDS, Sparx Systems DDS, and MilSOFT’s MilSOFT DDS.
DDS can scale to very large systems with a wide range of devices from microcontrollers to the cloud. It can be used to link devices for the IoT, and has been utilized in military Command, Control, Communications, Computers, and Intelligence (C4I) applications.