Reliable Connectors Keep Industrial Robotics Moving Efficiently
Download this article in PDF format.
Industrial robotics have been on the horizon for over a half a century, but now more than ever they’re transforming the industrial workplace. The industrial robot of today brings productivity, cost efficiency, and greater safety to their repetitive assigned tasks (Fig. 1). And behind the scenes of every effective and reliable robot is a myriad of scalable and flexible connectors to support these redundant, automatic, and/or remote robot activities.
Sponsored Resources:
- Manage, Monitor and Control
- Industrial Control Solutions - Controller/PLC
- Industrial Control Solutions - Signal
1. Stationary manufacturing robots require reliable, time-lasting connectors as they perform repetitive actions.
Common industrial mobile robotic technologies for detecting objects and obstacles include radar, cameras, optical, and ultrasonic. Radar, optical, and ultrasonic sensing transmit high-frequency waves into the atmosphere and around the circuits. Light and ultrasonic waves listen or watch for the echoes that reflect back from any obstacles. Radar sensors employ antennas to find reflected radio-frequency waves. Optical time-of-flight (ToF) sensors use a photodiode to capture reflected light waves from obstacles. So, it’s not surprising that as robotic technologies advance, so do complementary connector technologies.
This evolution of industrial robotics offers greater flexibility, range of motion, speed, functionality, and precision. For robots to operate in these complex ways, they must be able to collect and process a great deal of sensing data in hostile electrical and physical industrial environments. The task ahead is to identify and use highly reliable connectors for this industrial challenge. This article identifies a list of appropriate connectors to solve these problems
The Incredible Shrinking Connector
One challenge in this industrial environment is to facilitate the connection of data-bearing wire to a printed circuit board (PCB). In most cases, the data in these wires carry sensitive data with a hard connection for good continuity over time. The preservation of this continuity is vital in the midst of environment stress, such as temperature excursions, and mechanical stress, such as vibrations.
2. A Mini I/O connector firmly provides a foundation for this wire-to-PCB connection.
The design of TE’s Industrial Mini I/O solutions meets these stringent industrial environment demands. The compact, metal latching mechanism prevents accidental pull and/or un-mating, which reduces the possibility of system downtime. This small, compact connector is capable of latching in wire-to-board I/O interfaces, enabling it to meet stringent industrial demands (Fig. 2).
This connector uses 25% of the space required by conventional RJ45 plugs. The additional 75% of PCB space thus allows for greater design flexibility and increased application options.
In Figure 3, the TE Part # 2069578-2 enables IP20 wire-to-wire connections. To overcome high-vibration environments, the Mini I/O connectors are polarized and have two points of contact. The unique latching system offers two options available to prevent mis-mating. This latching system also protects the plug from pull out during high vibration and accidental bumping.
3. With the Mini I/O connector solution, up to 75% of board space is saved when compared to conventional RJ45 plugs.
Stable connections are guaranteed with the Mini I/O connectors, according to the company. The Mini I/O connector board-to-board reliable contacts allow for quick, easy modification and upgrade of equipment. The Micro-MaTch prevents unnecessary communication losses by dealing with the common industrial environment shock and vibrations.
The Industrial Mini I/O connector solution is intended to deliver reliable serial, bus, and Ethernet connections in industrial applications. Being just 25% of the size of a conventional RJ45, the system not only enables you to save on valuable board space, but with the reduced height, it makes it possible to build very compact DIN rail system modules.
The upgraded SMT PCB Mini I/O portfolio meets the latest industrial assembly process requirements. A reduction in solder paste improves co-planarity of 0.08 mm. In addition, the use of LCP materials in the connector allows for higher reflow solder temperatures. All of these factors increase processing efficiency and extend durability over the connector’s lifetime.
The Industrial Mini I/O connectors are more reliable than RJ45. Of course, their smaller size make for more efficient PCB design thanks to the space savings. In addition, the cause of an industrial environment’s downtime, which can be very costly, may be an unexpected network connection unplugging due to shock, vibration, or pulling cords. The Mini I/Os unique locking system is specified to 100N of pull force.
Fretting Corrosion Prevention
Fretting is wear or corrosive damage responding to the roughness of contact surfaces. This damage results under load and in the presence of repetitive surface motion conditions. Vibration can also cause a fretting condition.
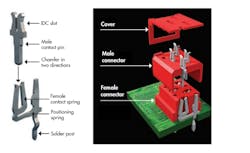
4. The connector socket has a contact spring system that acts to create a socket with fretting-corrosion resistance.
The traditional failure mode in tin-plated connections is fretting corrosion. The Micro-MaTch connector assists in preventing such corrosion. Because of the female part’s additional positioning spring, the Micro-MaTch connector absorbs relative vibration and thermal-expansion movements between male and female contacts. This configuration of connectors creates an airtight connection, as it prevents contact spot movements (Fig. 4).
The Micro-MaTch contact spring system is resistant to fretting corrosion. In this system, the positioning spring compensates positional tolerances and provides the tin-plated contact system’s high contact force
Contact spacing for the TE Micro-MaTch connector family is 1.27 mm (Fig. 5). Such spacing offers a variety of wire-to-board and board-to-board interconnection opportunities. Not only does the Micro-MaTch contact help prevent fretting corrosion in tin-plated connections it absorbs relative vibrations/thermal expansion movements between male and female contacts with an additional positioning spring in the female part.
5. The centerline Micro-MaTch 0.050 connector series is designed for PCB connections.
Conclusion
Today, manufacturing has to be more reliable, flexible, and connected. At TE Automation & Control, the delivery of innovative solutions make production more valuable. From the circuit board to the harshest working environments, along with the production floor and across the world, TE Automation & Control tries to make every connection count.
Sponsored Resources: