Discover New Bluetooth Applications with Mesh Networking
Download this article in PDF format.
Virtually all of us use Bluetooth. Headphones, speakers, beacons, hands-free devices, mice, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and hundreds of other similarly empowered devices. Bluetooth (BT) is also widely used in industry, smart cities, and building automation.
BT transceivers form wireless nodes for sensors and devices to be controlled. Most of those wireless links are either point-to-point or in a star network topology. Such connections work fine in small networks, but they have limitations if numerous nodes are needed. Those larger applications are often better served with a mesh network, a topology that wasn’t available to BT until recently. Now it’s possible to create large networks with BT.
Sponsored Resources:
- Getting Started with Bluetooth Mesh
- CYBT-213043-MESH EZ-BT™ Module Mesh Evaluation Kit
- EZ-BT Mesh Eval Kit - CYBT-213043-MESH Datasheet
What’s the Big Deal with Mesh?
A mesh network uses transceivers (called nodes) that can communicate with one another over a short-range point-to-point basis, but they also offer a repeater function. These nodes can relay messages that take the form of commands or data. If one node has a message for another node that’s out of wireless range, it sends the message through the network. That node then transmits its message to a nearby node that repeats it to another close node. The relay takes place until the desired recipient gets its message.
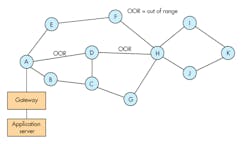
The figure shows a hypothetical mesh network. Assume all nodes are wireless sensors. Some of the nodes are within radio range of several other nodes, while others are more remote and out of range (OOR). Node A connects to a wireless gateway that transmits the sensor data collected back to an application server.
This is a hypothetical mesh network showing wireless links between nodes.
One of the main benefits of a mesh network is its reliability. If one node fails in some way, there’s usually another alternative path through other adjacent nodes. For instance, if node A wants data from node G, it can access it via nodes ABCG. If node D is out of range of A, it could still get the data from G by way of AEFHG.
The repeat capability lets you build large networks spread out over a wider area than normally served by a single wireless device. In factory automation, you can construct widespread monitoring and control nodes that span a huge area in a factory or plant. If you’re tinkering with some IoT application for home applications or building automation, you may want to learn more and shop around for mesh solutions.
Up to now, few wireless devices can implement a mesh network. Probably the most common is the Zigbee wireless standard that has been mesh-capable for years. Wi-Fi can now do mesh, and there are others like Thread. Today, Cypress Semiconductor offers its own Bluetooth mesh solution. Bluetooth with its long history of adoption and successful wireless connectivity gives engineers another proven option to work with.
Cypress Bluetooth
Cypress leverages the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) standard. These BT chips are easy on the power source, with low power consumption making battery operation the only rational choice for remote nodes.
Just as a review, BLE operates in the 2.4-GHz band with frequency-hopping spread spectrum and GFSK modulation. Data rates can reach to 2 Mb/s. While standard BT range is about 10 meters max, BLE can cover up to several hundred meters under the right conditions. And it includes encryption.
BT and BLE chips and modules must be tested and certified by the Special Interest Group (SIG). You should update your familiarity with BLE and BT in general by accessing their new publication Bluetooth Mesh Networking and others.
BLE is available as pre-certified modules that fully meet the Bluetooth SIG’s standards. The modules come with a wide range of options. For example, you can choose between a chip antenna, a PCB antenna, or no antenna, enabling you to customize to your application.
One really appreciated quality is the ease with which provisioning is accomplished. We have all had the BT pairing fun with our devices. Cypress features reduce that function to the point where it’s about as simple as possible. And don’t forget that all smartphones include BT/BLE, which permits the phone to act as a terminal and be a part of mesh network, if that makes sense in your application.
Here are some more specifics. To get started, select the Cypress’ Bluetooth SIG Mesh Evaluation Kit with four fully functional mesh nodes, mesh example projects, and iOS/Android reference mobile apps. Create your Bluetooth mesh network using the Cypress CYBT-213043-MESH Mesh Evaluation Kit. Called the Cypress WICED module, it’s a fully integrated, fully certified, programmable, dual-mode Bluetooth BR/EDR and low energy (BLE) module. It provides four node boards, each containing certified Bluetooth 5 CYW20819 modules, multiple mesh example projects, and iOS, Android, and Windows mobile helper apps.
Getting Started with Bluetooth Mesh
If you’re using BT, it’s essential that you check in with the Bluetooth SIG to access the standards and mountain of other helpful BT data. Then go get the Cypress application note that introduces Bluetooth Mesh and its key concepts, as well as describes how to get started with Cypress’ BLE Mesh solution to design your own BLE Mesh-enabled applications. With this combination, you can rapidly deploy successful BLE Mesh-enabled products with minimum development costs.
Cypress also has a new application note that introduces Bluetooth Mesh and its key concepts and describes how to get started with the its BLE Mesh solution to design your own BLE Mesh-enabled applications. The company offers a wide range of connectivity solutions for Internet of Things (IoT) applications plus a mix of silicon platforms with its widely deployed Bluetooth stack.
Sponsored Resources: