DC-DC Converter IC for ADAS Achieves Best-in-Class Stable Operation
If you’re concerned about tightening power-supply requirements in the automotive sector, your instincts are good. Technological innovation in accident prevention and autonomous driving is preparing the industry for a great upheaval, with market forces requiring miniaturization, robustness, and increased reliability.
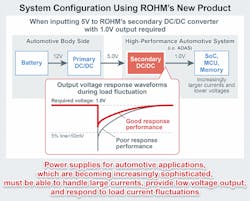
Near-future cars and trucks will not only perform better than today’s vehicles, but the high-tech community has gone on the offensive creating advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) SoCs and MCUs with increasingly sophisticated onboard sensors, cameras, and radars. These will require power-supply ICs that operate stably even under severe load-current fluctuation conditions.
Addressing this issue, ROHM developed the BD9S402MUF-C buck dc-dc converter IC with built-in MOSFET, which is targeted at automotive applications incorporating these onboard sensors. In addition to meeting the basic requirements of secondary dc-dc converter ICs in ADAS for 2 MHz or higher operation and 4-A output current, the part incorporates the company’s Nano Pulse Control high-speed pulse-control technology to deliver low voltage output down to 0.6 V—much lower than the typical 1.0-V voltage output required by current SoCs and MCUs.
Nano Pulse Control for monolithic (single-chip) dc-dc converters reduces the switching on time to 9 ns, said to be the smallest in the industry and a significant accomplishment considering that the typical on time is around 120 ns.
At the same time, the BD9S402MUF-C employs ROHM’s QuiCur high-speed load response technology for stable operation at what it claims is an industry-leading 30 mV (measurement conditions: 5-V input voltage, 1.2-V output voltage, 44-μF output capacitance, and load current variation 0 to 2 A/2 μs. This translates to a 25% reduction in output voltage fluctuation over standard products with equivalent functionality, suiting it for use in the latest ADAS with severe power-supply conditions requiring stable operation within 5%, even with low voltage output.
Delivering Stability
Generally, power-supply ICs constantly monitor the output voltage to ensure stable power-supply functionality and include a feedback circuit that fine-tunes the output voltage by comparing with an internal reference voltage. Providing faster response makes it possible to reverse changes in the output voltage caused by fluctuations in input voltage and/or load current in a shorter time.
On the other hand, shortening the response time too much can cause the circuit operation to become unstable and the output voltage to oscillate. Furthermore, because the response speed also is affected by output capacitance, until now it has been difficult to achieve the desired response performance.
QuiCur
Incorporating QuiCur in power-supply ICs reduces design resources by providing stable operation with fewer external components, making it possible to achieve the needed performance without causing instability in feedback circuits.
Not only can it reduce the number of external components and mounting area by minimizing the capacitance of the output capacitor required by the power-supply IC, but it enables linear adjustment of the capacitance and output-voltage fluctuations, ensuring stable operation even when the capacitance increases due to specification changes.
QuiCur is named after ROHM’s original “Quick Current” high-speed load-response circuit that maximizes load transient response characteristics without causing instability in the feedback circuits of power-supply ICs. Response performance equivalent to the company’s conventional products can be achieved with less than half the capacitance. Going forward, plans include expansion of its power-supply IC lineup incorporating QuiCur to support a wider range of applications.
Load Response
The BD9S402MUF-C also is equipped with a load-response performance selection function that leverages the characteristics of QuiCur technology. Users are able to switch priority between voltage fluctuation (for stable operation) and capacitance reduction (to ensure stable operation at 22μF) by setting High/Low of the GAIN pin.
For example, the user can set the GAIN pin to High for a power supply in a high-performance SoC that needs to handle fast load fluctuations. Or the GAIN pin can be set to Low for balance between performance and capacitor cost when the power supply for an MCU doesn’t need to consider high-accuracy voltage fluctuations. This significantly increases design flexibility for application designers, as stable operation can be easily achieved at initial design as well as during specification or model changes.
The BD9S402MUF-C includes built-in low on-resistance power MOSFETs in a VQFN16FV3030 package. Switching frequency is 2.2 MHz. The converter is priced at $2.00/unit (samples, excluding tax). Samples are available now; mass production is scheduled for April 2023.