NXP Unveils New One-Chip Radar for Autonomous Vehicles
This article is part of our CES 2023 coverage and the TechXchange: Automotive Radar
What you’ll learn
- How NXP is advancing radar sensors onboard vehicles.
- What NXP is offering.
- How the SAF85xx chip works.
As part of CES 2023, NXP Semiconductors announced a new 28-nm RFCMOS radar one-chip IC family for next-gen autonomous driving systems and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). The new SAF85xx one-chip family works alongside NXP’s high-performance radar sensing and processing technologies in one device to address short-, medium-, and long-range radar that meets more NCAP safety requirements.
“This advanced radar sensing technology plays an essential part in accelerating the development of next-generation ADAS,” said Mr. Hiroshi Kondo, Head of the Safety Systems Business Unit at DENSO Corp. “We know DENSO will extend its leadership position in ADAS by leveraging NXP’s compact high-performance SAF85xx radar SoC.”
Kondo added, “It integrates multicore radar processors which are built on NXP’s S32R radar compute platform.” The SAF85xx delivers double the RF performance and boosts radar signal processing by up to 40%. Its one-chip family achieves 4D sensing for the corner (200 m) and front (200 m+) radar, serving safety-critical ADAS applications (Fig. 1). Meanwhile, the multicore processor delivers 1.5X compute. It also can provide elevation measurement for the 360-degree radar cocoon.
The SAF85xx 1-chip provides a longer range with its 15-dBm power output and 10.5-dB noise figure. It also comes with improved object/VRU identification and separation thanks to the −96-dBc/Hz phase noise rating (Fig. 2). Other notable specifications include the ADC sample rate (80 Msamples/s) and chirp bandwidth (5 GHz) for accurate distance resolution. The 7-bit phase rotator achieves enhanced multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) waveforms. Lastly, it offers exceptional thermal performance, operating in temperatures reaching 150°C.
“Our new radar one-chip family enables the reliable long-range detection of objects and separation of small objects next to larger ones, like a fast-moving motorcycle next to cars and trucks on a busy multi-lane highway,” said Torsten Lehmann, Executive Vice President, NXP Semiconductors. “Its small form factor allows our customers to build radar sensor modules that are up to 30% smaller, enabling global suppliers of ADAS systems, like DENSO, to expand the potential of radar safety through this powerful new technology.”
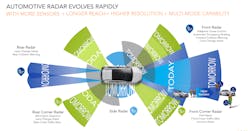
Additional sensors, extended reach, higher resolution, and multi-mode capability make it possible for the automotive radar to evolve (Fig. 3). The rear radar features lane-change assist and rear-collision warning assist capabilities. Meanwhile, the rear corner radar provides blind-spot detection, lane-change assist, and rear cross-traffic alert. The frontal radar has adaptive cruise control, automatic emergency braking, forward-collision warning, adaptive braking, and lane-change assist. And the front corner radar provides park assist, junction assist, and front-cross-traffic assist.
The 77-GHz SoC transceiver has a Gigabit Ethernet communication interface, four high-performance transmitters, four receivers, unique architecture, and algorithms. It includes a multicore radar processor with hardware accelerators for 64X performance versus standard cores, consumes little power, and uses radar algorithms to boost performance.
This article is part of our CES 2023 coverage and the TechXchange: Automotive Radar