Taking More Steps Toward Adopting 800-V Systems for EVs
This article is part of the TechXchange: EV Battery Management.
What you'll learn:
- Benefits of 800-V systems.
- BorgWarner's new 800-V inverter.
- The highest-voltage (800 V) wireless BMS, developed by LG Innotek.
Although the high-voltage circuitry in electric vehicles (EVs), such as the electric compressor, dc-dc converter, etc., is built up around a 400-V system, 800-V alternatives are making a rapid rush to the head of the line. Among the reasons are the efficiency benefits achieved by using an 800-V dc bus voltage and wide-bandgap silicon-carbide devices rather than a conventional IGBT inverter and a 400-V dc bus. Another key reason is faster charging. Generally speaking, doubling EV voltage means that the time to charge up the battery pack is effectively halved.
Two examples of this trend were announced recently in the same week. First, BorgWarner is building upon its current 400-V inverter business with a major (unnamed) global OEM by also supplying 800-V SiC-based inverters.
Second, LG Innotek has developed an 800-V wireless battery-management system (BMS) that combines the essential components for wireless communication into one module that’s said to be compatible with all communication chips. Improving the BMS by going wireless reduces the weight of the system, allowing for more energy efficiency and thus increasing the car’s driving range with the same charge.
High-Voltage Inverters
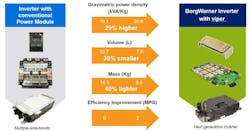
BorgWarner’s scalable high-voltage inverters are destined for battery-electric-vehicle (BEV) platforms. Two variants will be used in passenger BEVs—a 250-kW module for passenger cars and all-wheel drive crossover utility vehicles and a second 350-kW version for the OEM's performance vehicles.
Viper is the first 800-V inverter to use a double-sided, cooled, SiC-based power switch. It delivers the higher power densities and efficiencies needed to extend battery range and performance, and it reduces costs.
"As a current 400-V inverter supplier to the automaker, it was a significant win for our team to be brought on for the 800-V program as well," said Dr. Stefan Demmerle, President and General Manager, BorgWarner PowerDrive Systems. "This expanded business solidifies BorgWarner's position as a strategic inverter supplier for this longstanding customer as they transition to the next phase of their BEV strategy."
Leveraging BorgWarner's Viper-based family of silicon and SiC power modules, the company says it can deliver 400- and 800-V inverters that offer lower mass, higher efficiencies, scalability, and higher power densities. Ranging from 150 to 350 kW, BorgWarner further says its inverters can be customized to fit customer needs.
Start of production for the new inverter program is 2025, with peak annual volume nearing 400,000.
Wireless BMS
A BMS is an essential component for electric vehicles. It monitors the voltage, current, temperature, etc., of a battery in real-time to optimize the performance and lifespan of the battery. When the BMS receives data from a battery cell, the electronic control unit (ECU) of the vehicle controls the power input/output according to the state of the battery cell.
Most EVs produced up to now have wired BMSs on them. Multiple BMSs are connected via copper cables (a wire harness) inside a battery pack. Because of this, the cables and connectors occupy a significant portion of the battery pack's volume and weight.
According to LG Innotek CEO Jeong Cheol-dong, the company has succeeded in developing a wireless BMS that improves battery performance
The new product employs 800 V, which is the highest voltage among commercially marketed BMSs. The company had already succeeded in developing an 800-V wired BMS in 2020.
LG Innotek’s wireless BMS is embedded with a radio-frequency (RF) communication module. The module combines essential components for wireless communication, such as an RF communication chip and antenna, into one unit.
The key advantage of going wireless is that it contributes to reducing the weight of vehicles mounted with a BMS. Once the cables connected to the BMS are removed, vehicle weight is reduced by 66~198 Ib., according to the company.
Eliminating the dozens of cables and connectors required for a BMS also reduces the volume of the battery pack. This secures 10~15% of additional space for a battery pack, enabling an increase in battery capacity.
Put another way, it can increase the mileage of an EV: It’s been confirmed by LG that a wireless BMS extends the mileage of an EV by up to 12 miles. Furthermore, the additional space for a battery pack improves the flexibility of battery design and allows, for example, changing the battery-pack structure, boosting the added value of this item.
LG Innotek also has implemented an inspection system for checking the BMS’s communication performance, enhancing the design convenience for its customers.
What’s more, the adoption of a wireless BMS further enhances the reliability of the product. First, the possibility of cable or connector defects due to the shaking of the vehicle will completely disappear. In addition, the assembly of a battery pack, previously conducted manually due to the complexity of cable connections, can now be automated using a robot, achieving a cost reduction.
To wirelessly send and receive data for an EV battery, the wireless BMS must be equipped with dozens of components, such as an RF circuit, RF communication chip, and an antenna.
Above all, the RF communication module mounted on the company's wireless BMS is designed to be compatible with all types of communication chips. This compatibility enables the application of the company's wireless BMS to all EVs produced by its clients.
On top of that, LG Innotek said it established a simulation technology for the first time in the industry that enables virtual inspection of wireless communication quality on its own at the development stage of a battery pack.
The company's virtual inspection system has proven its effectiveness by showing that predictions it made regarding communication quality of wireless BMSs had matched the actual measurement results by more than 95%. The company's virtual inspection system ensures only products that passed the inspection to be provided to its clients. Thus, it eliminates the need for automobile and automotive component manufacturers to request a separate inspection test.
LG Innotek plans to start mass production of the wireless BMS in 2024. The company also plans to start the development of an electric-vehicle charge controller (EVCC) wirelessly by leveraging the technology acquired by the company.
It’s expected that major global automobile companies will adopt a wireless BMS starting the year 2024. According to industry sources, the size of the global related market, which was only US$7.16 million in 2022, is expected to grow to US$1.1 billion in 2028.
Read more articles in the TechXchange: EV Battery Management.