High-Temp Power Inductors Ease into LED Headlight Apps
TDK Corporation recently expanded its lineup of metal core power inductors with the new SPM-VT series designed especially for the high thermal and current demands of automotive LED headlights. These wire-wound power inductors offer an operating temperature range of -55 to +155°C and high rated currents of 4.7 to 36.6 A (ISAT), depending on type.
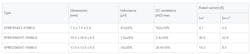
The new components are qualified to AEC-Q200 and initially come in three sizes: 7.5 x 7.0 x 5.4 mm, 10.5 x 10.0 x 6.5 mm, and 13.0 x 12.5 x 6.5 mm. Their rated inductances range from 1 to 47 µH, depending on type. Mass production starts in September 2019.
The SPM-VT series is based on TDK’s metallic magnetic material technology that allows for a high magnetic saturation density and robust structural design. The metal core power inductors offer dc superposition characteristics in a compact size and feature a rated current that is approximately two to three times higher than that of comparable high-temperature products based on ferrite core materials.
Modern adaptive LED headlights typically use one and the same control circuit to drive all LED headlight functions such as low and high beams, daytime running lights, and curve lighting. Thanks to their low power consumption and multifunctionality, LED headlights are now rapidly replacing conventional halogen and HID headlights. The dc-dc converters in the power circuits of LED headlights use power inductors, and as the functionality of the headlights increases, the number of inductors needed also grows. According to TDK, the new SPM-VT series meets the automotive industry’s demand for compact, high-performance power inductors that can support high currents and withstand high temperatures. The company will continue to expand the SPM power inductor lineup to include more miniaturized inductors with dimensions of 7.0 x 6.5 x 4.5 mm and 5.3 x 5.1 x 3.0 mm, for example.
Main Applications
- Automotive LED headlights
- Power circuits for various automotive electronic control units (ECUs)
Main Features and Benefits
- Operating temperature range of -55 to +155°C for high heat resistance in automotive LED headlight applications
- Superior dc superposition characteristics based on metallic magnetic materials
- Rated current approximately two to three times higher than comparable ferrite-core power inductors
- Qualified to AEC-Q200
Key Data
* Isat: Based on the inductance change rate (30% lower than the initial figures)
** Itemp: Based on a temperature increase of 40 K