How is Artificial Intelligence Affecting Your Job?
What you’ll learn:
- How are artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) affecting engineers?
- What engineers think about AI/ML.
- Does AI/ML have an impact on new designs?
A number of questions in our annual salary survey focused on the impact of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) and how they relate to engineers’ jobs, as well as what engineers think about the technology.
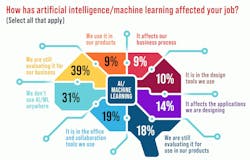
To start with, we asked how artificial intelligence/machine learning has affected their job (Fig. 1). The largest number of respondents are still evaluating AI/ML, while a significant fraction isn’t involved with it at all. Only a few use it in their products at this point, but more are incorporating the technology into their development process and products.
Part of the challenge is defining the AI/ML tools and frameworks currently out there and figuring out how they can be used. A lot of the generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, continue to evolve but are harder to evaluate and include in the development process.
The more successful uses of AI/ML tend to be in models based on more established and focused technologies like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and frameworks such as TensorFlow that have a proven track record and support infrastructure. They typically have fewer problems, e.g., hallucinations, that often occur with large language models (LLMs). Many can also be handled by smaller, embedded systems, although even LLMs are making their way into mobile devices, albeit with significant hardware acceleration.
>>Check out this TechXchange for similar articles and videos
How Engineers Feel About Artificial Intelligence
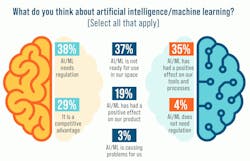
Engineers’ thoughts about AI/ML are reflected in our results (Fig. 2). While it can be a competitive advantage, more think regulation is necessary and that it should be unregulated. Only a small percent of them have run into problems using AI tools or frameworks. However, a significant number aren’t ready to utilize or incorporate machine learning into their processes or products. That’s not surprising given the prior chart where a significant number of engineers remain in the evaluation stage.
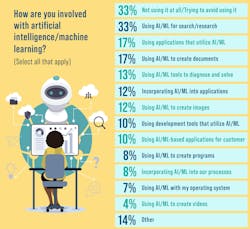
When we asked how engineers were using AI/ML we received a range of responses (Fig. 3). A third of the respondents weren’t employing any tools or even avoiding them for now. Another third uses it via search engines. These days, that’s almost hard to evade. Worse, many of the search engines implement generative AI by default.
A few use tools to create text, images, videos, and software, but we didn’t ask additional questions or get more detailed responses in how these were applied, what the quality of results were obtained, etc. We will probably add questions along these lines in the future, as much of this usage may be in the realm of evaluating the tools and solutions rather than incorporating them into the design and production process.
Impact of AI/ML on Engineers
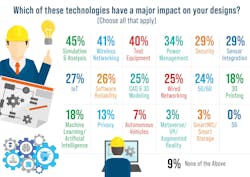
AI/ML was at the low end in terms of technologies that had a major impact on engineers and designers (Fig. 4). It’s not surprising given the answers to the previous questions. The number was up slightly compared to last year.
What I found surprising was the importance of simulation and analysis, given that it was a new question this year. Wireless networking, test equipment, and power management remained at the top. We will keep an eye out to see if AI/ML moves up next year.
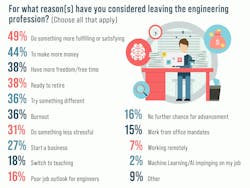
One other area where we added AI/ML amongst the questions concerned whether an engineer might consider leaving the profession (Fig. 5). At this point, it doesn’t seem to have a significant effect. This may change over time as AI/ML becomes more mainstream in the development process or in the tools and frameworks used by developers. I suspect, though, it will be a good while before AI/ML becomes a replacement or challenge to engineers rather than a tool to improve our effectiveness.
>>Check out this TechXchange for similar articles and videos
About the Author
William G. Wong
Senior Content Director - Electronic Design and Microwaves & RF
I am Editor of Electronic Design focusing on embedded, software, and systems. As Senior Content Director, I also manage Microwaves & RF and I work with a great team of editors to provide engineers, programmers, developers and technical managers with interesting and useful articles and videos on a regular basis. Check out our free newsletters to see the latest content.
You can send press releases for new products for possible coverage on the website. I am also interested in receiving contributed articles for publishing on our website. Use our template and send to me along with a signed release form.
Check out my blog, AltEmbedded on Electronic Design, as well as his latest articles on this site that are listed below.
You can visit my social media via these links:
- AltEmbedded on Electronic Design
- Bill Wong on Facebook
- @AltEmbedded on Twitter
- Bill Wong on LinkedIn
I earned a Bachelor of Electrical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and a Masters in Computer Science from Rutgers University. I still do a bit of programming using everything from C and C++ to Rust and Ada/SPARK. I do a bit of PHP programming for Drupal websites. I have posted a few Drupal modules.
I still get a hand on software and electronic hardware. Some of this can be found on our Kit Close-Up video series. You can also see me on many of our TechXchange Talk videos. I am interested in a range of projects from robotics to artificial intelligence.