GL announces simulation of location-based services in mobile networks
GL Communications announced today the release of its LoCation Services (LCS) Test Suite, which comprises multiple products working in tandem to support simulation of end-to-end location-based services in GSM, UMTS, and LTE networks.
Karthik Ramalingam, a senior manager for product development at the company, said, “Location-based services provide information about the geographic location of mobile equipment (ME) and are widely used in social networking, vehicle tracking, stolen-assets tracking, emergency services, and many more. The information is expressed in latitude and longitude data that is represented in a well defined universal format.”
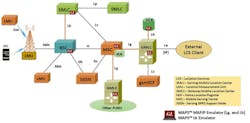
He added, “The LoCation Services (LCS) architecture follows a client/server model with the Gateway Mobile Location Centre (GMLC) acting as the server node providing information to external LCS clients. All LCS clients communicate with this node to request positioning information. Additionally, the GSM network includes separate nodes, a Service Mobile Location Centre (SMLC) that resides within BSC, and location measurements units (LMU) that resides within the BS, for calculating and updating the location measurements.”
He continued, “Specifically, to test location services in a GSM network, GL’s MAPS MAP IP signaling emulator is enhanced to simulate LCS procedures over Lg and Lh interfaces using the MAP signaling protocol. The MS-initiated Location Report Procedure is supported over Lg Interface between the GMLC and the MSC, and network-initiated Location Retrieval Procedure is supported over Lh Interface between the GMLC and HLR.“Further, the MAPS Lb interface emulator supports a Location Service Request procedure over Lb interface between the BSC and SMLC using BSSMAP-LE signaling protocol.
“GL’s MAPS supports simulation of different positioning methods and position estimation of a mobile station (MS) in universal coordinates. The estimate is expressed in terms of the geographical shapes and is composed of the type of shape plus the encoding of the shape itself. The Location Estimate parameters such as type of shape and coordinates can be input through conventional user profiles or can be fetched from a CSV file every time it sends the location estimate to the client. This selection is to be made by the user.
“If the selection is ‘Profile’ all the values present in the particular profile will be sent in the message response. If the selection is made as ‘CSV’, an entry from the csv file is loaded and all the values from the fetched record will be sent in the message response.
“These coordinates indicate different position of MS at different intervals of time and report is sent either periodically at specified time duration or at once when requested.”
http://www.gl.com/test-location-based-services-lbs-wireless-networks.html