What you'll learn:
- Integrating motion processing into mobile gaming.
- What does the X7 post-processor deliver to gaming and other applications?
- Who is Pixelworks?
Video processors have used frame interpolation systems such as motion estimation (ME) and motion compensation (MC) for decades. However, typical solutions are power-hungry and introduce interpolation errors.
Pixelworks, a video alchemist skunkworks in San Jose, has been quietly developing a new, back-end mobile processor that works for both movies and now, video games. The result is an incredibly brilliant image, at super high resolutions and high frame rates, but with minimal latency that can actually improve battery life as well. It sounds almost as if they have broken the law of physics. But, no, says their CEO, we just know those laws very well and how to work within them.
Secret Sauce
By using an expert-trained video motion estimation and compensation algorithm in silicon for video-frame interpolation, the company has pushed the bounds limiting performance or quality. Through a novel adaptive compensation scheme trained by the company’s picture-quality experts (that the company doesn’t want to talk too much about), Pixelworks has integrated motion processing—things they’ve done for the film and TV industry in software—into a mobile gaming solution that’s now possible in a smartphone.
This secret sauce, the expert training by their best engineers and picture-quality people, is differentiable such that the flow and estimation can be optimized jointly in real-time, and very fast, with minimal latency. In addition to the Smart MEMC, the design can be seamlessly adapted to several other video-enhancement tasks such as super-resolution, denoising, and deblocking.
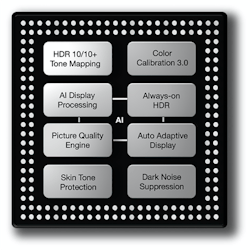
Quantitative and qualitative evaluations and demonstrations have shown the X7 post-processor (Fig. 1) outperforms state-of-the-art video-frame interpolation and enhancement algorithms on a wide range of datasets. Compared to existing methods, the X7’s magic is computationally efficient and able to generate more visually appealing results.
The Impact on Gaming
One segment appreciative of that is gaming, and as most people know, gaming has become a big business in units and dollars worldwide. It’s especially big in China, where it’s estimated there are 670 million gamers—20% of the world’s estimated 3.3 billion gamers. Most of those gamers play on a smartphone.
Chinese gamers have adopted Genshin Impact as a benchmark. One of the elements in the game is weather. Weather is an exploration mechanic. While exploring the world, the weather can shift. Depending on the new weather conditions, special properties will be applied to the environment, to the characters, and to opponents.
Games like Genshin Impact, and PC games like Cyberpunk 2077, which have been ported from the PC to smartphones, challenge the phone’s performance versus battery and heat operating parameters. Big games demand everything the phone’s processor has to offer, and in the process, runs down the battery while heating up the phone.
Pixelworks saw that as an opportunity to apply its magic and introduced the X7 chip architecture, post-processors that exploited some of the techniques the company used in the film and TV industry. The X7 chips created a new distributed computing/rendering chip market segment in mobile; a bit like what AMD and NVIDIA have done in the PC and console segments. Chinese phone manufacturers have referred to X7 as standalone display solution, a render accelerator, or a dual-chip gaming architecture.
Meeting Performance Demands
MEMC and resolution scaling (SR) are very demanding on any platform and especially in a mobile device with limited cooling and power supply. The phone must deliver a high frame rate, with high color accuracy, high pixel resolution, no artifact or aliasing, and low latency, and accomplish all of that while using very little power.
Pixelworks’ post-processor has proven to be just what the doctor ordered, a unique technology for motion compensation and SR that offloads the phone’s SoC (Fig. 2). Specifically targeting gaming by taking care of the motion vectors and working with game-engine developers, the X7 processor uses metadata that enables a guarantee of the best gaming experiences.
As a result, three out of four of the largest Chinese phone OEMs have been shipping their top phones with Pixelworks’ chips. The leading game-engine providers (e.g., Unity) have been partnering with Pixelworks, the big game studios in China (ByteDance, Tencent, miHoYo, etc.) have engaged with Pixelworks, and mobile SoC processor makers such as MTK and Qualcomm are working with Pixelworks.
The X7 is a tiny chip and draws so little power that the smartphone hardly knows its running. Some smartphone suppliers in China have already added it to their phones to placate their game crazy-customers, and if one can satisfy that price-performance market segment, then they must have something special.
This is a classic story of a smallish (~$70 million in revenue) company quietly working in close collaboration with some big name and colossally demanding customers and perfecting a solution that is scalable, efficient, and economical.
The Pixelworks Story
Pixelworks didn’t just stumble into this market. Founded in 1997, the company developed video processors for professional projectors. The video engineers and scientists at the company had a collective range of experience unmatched in companies many times their size.
However, they were techno-geeks, not salesmen. You almost had to know someone who knew someone to find out about them. Their customers weren’t eager to reveal them either—Pixelworks was their secret sauce and how they differentiated themselves in a cut-throat take-no-prisons business.
The mythology of the company is the CEO or CTO (the story varies depending on who is telling it) was chatting at a conference with a CTO or president of a phone company and he said, “It’s my dream that someday we will have smartphones that you can watch a movie on, and it will be as good as if you were in the theater.” The Pixelworks guy went home thinking about that and the next day he told his team, “I’ve got an idea.”
A few years later, visiting the lab (if you could get in), one could see a big 4k screen showing video and games as if it was driven by an enthusiast-level PC. But it wasn’t—it was driven by a two-year-old smartphone and not even a top-of-the-line smartphone.
The term skunkworks isn’t used lightly here. Pixelworks has managed to beat out the top SoC builders in Silicon Valley and San Diego in video processing. In one sense, that’s not too surprising—video is all they do. Today’s smartphones are a marvel of technology, but they can’t be the best at everything they do. Product cycles and R&D budgets mitigate how much they can invest in time and dollars.
Pixelworks is a specialty company—a pixel polisher. They also can polish pixels coming from the sensor, but they acknowledge the big SoC builders had done a really good job with their integrated ISPs. The CEO told me “you climb one mountain at a time.”
The tantalizing end of this story is the future. Pixelworks has now proven their bespoke approach to video processing—pixel polishing works. In fact, it works almost better than they thought it would. And it’s scalable. It will ride Moore’s law and just get better with each generation. Smartphones have (or will) never looked so good.