How are AI Chips Making the World a Smarter Place?
What you’ll learn:
- What are the different components of AI chips and how do they function?
- What are the differences between CPU, GPU, FPGA, and ASIC chips?
- How are AI chips beneficial in robotics, NLP, wearable technologies, retail, and healthcare?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are the next best technologies to hit the electronics industry, finding applications in all sectors. Helping spur this growth are AI chips.
Now in the age of Web 3.0, is seemingly pervading everywhere. It’s seldom now that you visit a website without chatbots, or you buy a phone with no access to an assistant. Going a step further, the production of AI chips with AI accelerators and the capability of deep learning has become a focus of many chipmakers. The growth of AI chips has ramped up to the point where Stratview Research, projects the artificial-intelligence chips market to grow from USD 10.81 billion in 2021 to USD 127.77 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of around 42.30% (Fig. 1).
What are AI Chips?
Artificial-intelligence chips are pieces of hardware that have a very specific architecture to support deep-learning-based applications through AI acceleration powered by specially integrated accelerators. They’re in demand because of their special ability to turn data into information and make that information into knowledge to work upon. In addition, they function through several computer commands and algorithms that help them initiate activity and brain structure.
An important aspect of these chips is deep learning. Deep learning is a part of machine learning that has exceptional AI applications—it’s also known as a deep neural network (DNN) or active neural network (ANN). DNNs learn from already available data during the training phase and can make predictions from new data later. These networks make it easier for the chips to collect, analyze, and interpret large amounts of data in a very short span of time.
Why Do We Need AI Chips?
It all started when central processing units (CPUs) were central to the proliferation of personal computers. It was the brain of the computer and performed basic arithmetic, logic, and control operations for the computer.
However, gradually came the need for processing real-time 3D images, which the CPU wasn’t quick enough to handle. Thus began the era of the graphical processing unit (GPU). It replaced the CPU and fulfilled the demands quick and efficient 3D image processing.
Now the time for the quick processing of AI applications has arrived. And although GPUs can process AI applications better than CPUs, they’re not perfect. They can execute AI models but are fundamentally optimized for processing graphical models and not neural networks, creating a demand for the artificial-intelligence processing unit (AI PU).
The AI PU acts as the AI accelerator on AI chips. It can accelerate the computation speed of ML tasks by nearly 10K times more than the GPUs. In addition, the AI PU is capable of better resource utilization as well as being more power efficient when compared to CPUs and GPUs.
The AI PU is just one of the components that are present in an AI System on Chip (AI SoC), though.
Components of an AI System-on-Chip
Neural Processing Unit
The NPU, also known as the AI PU, is the chip’s brain. It’s the most important component of the chip, which makes any chip different from others in the market. The NPU has the power to compute data quickly and efficiently with less utilization of power.
Controllers
Controllers are the processors that control the chip’s activities and keep them in sync with the other components on the chip as well as with the external processor.
SRAM
SRAM answers the question of where to store the AI models or intermediate inputs on the chip. Also known as static random-access memory, it can quickly and conveniently store all of the models, which can be accessed in no time when needed. However, there’s just one catch: It doesn’t have a large storage space like dynamic RAM (DRAM) outside of the chip.
Input/Output Blocks
I/O blocks on the chip are extremely important in the inner workings of the SoC. They connect the components on the chip with external components such as DRAM and the external processor. These blocks aid in maintaining the flow of data and keeping the exchange between the external and internal components streamlined.
Interconnect Fabric
Just like I/O is important in maintaining the exchange between internal and external components, interconnect fabric specializes in the connection and exchange between just the components on the AI chip. Essentially, it makes or breaks the efficiency and speed of the chip. It's crucial that it keeps up with the speed of other components and doesn’t create latency, which can adversely affect the chip’s performance.
Though not as perfect as the designs of CPUs and GPUs, rapid advances in AI chips are bringing them closer to that level. For instance, in 2021, Cerebras launched the CS-2 with 850,000 processing cores and 2.6 trillion transistors. According to the company, the AI chip is 10,000X faster than GPU chips. In other words, the AI neural networks that previously took months to train on GPU chips can now train in minutes on the Cerebras system.
Advantages of AI Chips Over General Hardware
Quicker and Efficient
Artificial-intelligence models require faster parallel-processing abilities from the chips to aid overall performance and not act as a bottleneck. AI chips provide parallel processing that’s 10X higher in ANN applications when compared to traditional semiconductor devices, at a similar price.
In addition, they’re better suited to the heterogenous computing that’s required nowadays, with its low-power consumption and high performance.
Higher Memory Bandwidth
When we talk about parallel-processing capability, the chips are required to allocate more memory bandwidth for AI models to process smoothly. AI chips are superior in this regard, as they allocate 4X to 5X more bandwidth for computing purposes.
For instance, the newly launched AI chip called NeuRRAM has 48-core, RRAM-CIM hardware that’s more than 4X the memory available in the Intel CPU Core i5-13500, which boasts 10 to 16 cores.
Speaks to New Technological Demands
The new-age AI chips are specially designed to work with AI and ML to develop smarter devices for human use. With multiple processors and their specialized functions, AI chips have an upper hand in dealing with new-age technologies when compared to the traditional options.
Different Types of AI Chips
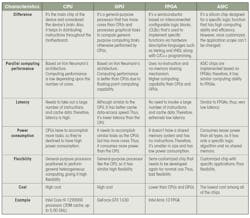
Figure 2 and the table illustrate and detail the four main types of chips: application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), central processing units (CPUs), and graphical processing units (GPUs).
Applications for AI Chips
- Robotics: With the continuous need for hardware advances in state-of-the-art robots, AI chips are sure to make a world of difference. They also can power applications in computational imaging for drones, etc.
- Wearables: AI is a tremendous asset when it comes to wearable technologies. For instance, AI can assess speech patterns, moods, and heartbeats and inform the user with warning signals. In addition, it helps the user improve performance in sports, etc.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Demand for analyzing user conversations and messages is growing due to the rise of chatbots, assistants, and online messengers such as Whatsapp, Slack, etc.
- Computer vision: In-vehicle assistance from computers is another application that’s quickly ramping up. Major companies like BMW, Ford, and Tesla are banking on the security aspect by aiding the driver using AI. And, of course, autonomous cars are undergoing continuous testing using the combination of AI and ML. For example, in May 2022, Intel announced that it was leveraging Habana’s AI chips to train self-driving cars.
- Retail: Apart from the security systems at shopping malls, it helps retail market with material storing, shelf management, storage management, and transport.
- Healthcare: Assessing and monitoring patients’ health forms is a big part of treatments for patients. AI warns healthcare workers about the deterioration of a patient’s health, quickly alerting them to provide proper treatment.
A Look Ahead
One trend in AI is the move toward adopting neuromorphic chips in high-performance sectors such as the automotive industry. On that front, major players like Intel and NVIDIA are vying for a larger share of the neuromorphic chips market.
For example, in Oct 2021, Intel launched its second-generation neuromorphic chip, Loihi 2, and an open-source software framework, Lava. These advances are intended to drive innovation in neuromorphic computing, leading to its better adoption.
AI chips also are getting lots of play in the automation industry, making it the secret sauce for them to build smart homes and smart cities.