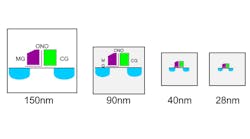
As automotive engines move to ever-lower fuel consumption, new control mechanisms must deal with new control mechanisms and system downsizing. This requires high-speed real-time processing (e.g., dynamic switching between multiple control algorithms) and three to five times greater performance in flash MCUs. To meet those demands, Renesas Electronics says it’s developed the first 28-nm flash memory intellectual property (IP) for microcontrollers (MCUs) using 28-nm process technology. Single-chip MCUs developed with the new technology will be able to support a maximum capacity of over 16 Mbytes of flash memory on-chip. The latest 28-nm prototype chip achieved a 160-MHz readout operating clock frequency, a data-retention time of 20 years, and rewrite cycle count of 250,000 cycles (for data storage). To create the prototype, the company exploited the scalability of the MONOS (Note 1) structure flash memory, which made it possible to increase the capacity and performance of the memory integrated in flash MCUs. For the automotive industry, the 28-nm flash memory IP enables support for complex 3D-radar data processing to increase safety. Also, in the powertrain area, it allows for even finer-grained control of fuel injection and ignition via increased mapping data.
Comments