Walking the Development Tightrope: Balancing Innovation and Safety in Robotics
What you’ll learn:
- Issues related to operating systems and open-source software.
- Real-world implications and future trends of safety and security support.
No longer a distant dream, next-generation robotic applications are revolutionizing countless aspects of our world—from surgical robots and underwater inspection bots to AI-driven waste-management systems and everything in between. Once relegated to the realm of science fiction, these advances promise unprecedented efficiency and safety.
Still, the industry faces a critical challenge: How to balance rapid innovation with stringent safety and security requirements. If the field of robotics continues its unrelenting march to transform sector after sector, the prioritization of both safety and security will be paramount to realizing its full potential while protecting developers and end-users alike.
The Software Pressure Cooker: Innovation vs. Safety
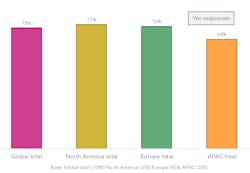
Make no mistake, this idealized future is far from certain. BlackBerry QNX recently commissioned a global survey of 1,000 embedded software developers and engineers (including 158 who work in the robotics industry), which revealed that 75% of respondents admit that the urgency to deliver projects on time often leads to compromises on key safety aspects (see figure). That staggering stat should give pause to anyone considering implementing robotic systems in their manufacturing processes or swapping out their old vacuum cleaner for a robotic one.
Furthermore, while “security,” “cost control,” and “safety certifications” were called out as the “top” considerations for developers when selecting an operating system (OS) for their applications, 61% of respondents said that they found it challenging to achieve the necessary safety standards with their current OS. And nearly a third admitted they didn’t have these measures in place at all, or they only had partial coverage.
Operating Systems and the Open-Source Dilemma
Though open-source operating systems are favored by nearly half (44%) of developers, primarily due to their widespread familiarity and open availability, these platforms are more likely to experience breaches (46% vs. 40% for proprietary systems), leading to project delays for 72% of those affected. This underscores the need for pre-certified, secure-by-design solutions that enable developers to focus on innovation rather than troubleshooting.
Check out the video for more details about the survey:
Real-World Implications and Future Trends of Safety and Security Support
Amidst this challenging backdrop, and as we look ahead in 2025, the robotics industry is poised for profound change. New applications, stricter safety standards, and closer cooperation between humans and machines are driving the next level of technological progress.
Safety remains a paramount concern, especially in collaborative environments where humans and machines work together. The expected publications of the revised ISO 10218 and ISO 13482 will set a new standard for industrial and service robots.
Robotics will continue to dominate in "dull, dangerous, or dirty" tasks—e.g., polishing a painted surface, or conducting inspections, repairs, and maintenance in high-risk environments—reducing the potential for human injury or accident and increasing efficiency.
Indeed, many of these systems are already in use and expanding to include more applications, for functionality like recycling process improvements. In waste management, for instance, robots equipped with AI vision systems are being deployed to identify and sort various types of waste materials. In healthcare, robots deliver meals and medicines in hospitals, avoiding obstacles and proactively detecting maintenance needs. These systems relieve staff from routine tasks, allowing them to focus more on patient care.
In addition, modern production lines are using software to restrict movements when a person is in close proximity. As a result, robots can dynamically react to human movements, further reducing the risk of shop floor accidents.
The Role of Sensor Fusion and Autonomous Mobile Robots
The transfer of technologies from the automotive industry to autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) is another exciting development. Sensor fusion, which combines data from multiple sensors, enables precise navigation essential for both autonomous vehicles and large warehouse robots. AMRs in logistics centers can sort and transport parcels more efficiently by safely avoiding obstacles and optimizing routes.
Industry 5.0: A Harmonious Collaboration
Looking further afield, the vision of Industry 5.0 is one of harmonious collaboration between humans and machines. In agriculture, drones with high-precision sensors can detect problem areas, while farmers monitor and intervene remotely. Autonomous systems can apply seeds, pesticides, fertilizers, and water more efficiently, saving time and optimizing yields. This symbiosis between man and machine represents the future of robotics, where innovation and safety go hand in (robot) hand.
BlackBerry QNX's recent research shows that there’s still significant room for growth in achieving this utopian future, which is by no means a fait accompli. For the robotics industry to fully realize its potential, developers must ensure they balance the necessity of innovation with the non-negotiable demands of safety and security.
By addressing these challenges head-on, the industry can pave the way for a future where robotics not only revolutionizes industries, but it also enhances safety and quality of life for everyone.
About the Author
Winston Leung
Senior Manager, QNX
Winston Leung is a seasoned innovation strategist with over a decade of experience advancing technology and driving business development in public and private sectors across North America and Asia. Specializing in transformative industries like transportation and robotics, he has led initiatives in autonomous, connected, and electric vehicles, developing policies and strategies to support their adoption. Winston’s notable achievements include spearheading Canada’s first connected vehicle testbed and guiding go-to-market strategies for emerging technologies, including quantum, 5G, and more.
Currently a Senior Manager at QNX, Winston delivers strategies and thought leadership in functional safety, real-time performance, and reliability for embedded systems across robotics, medical, and transportation sectors. He has collaborated with international stakeholders, influenced government policies and driven startup success. Combining technical expertise with strategic insight, Winston is shaping the future of autonomous and robotics technologies through innovation and impactful leadership.