New FPGA Board Targets Exascale Applications
See more TechXchange Talks videos.
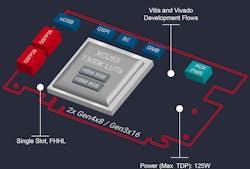
The Xilinx Alveo U55C FPGA board (Fig. 1) targets exascale applications in the cloud. It's designed to share workloads across multiple cards and employs high bandwidth memory (HBM) on-chip. The single slot, half-length card consumes only 125 W.
The passively cooled, PCI3 Gen3 board (Fig. 2) sports a pair of QSFP28 interfaces providing SmartNIC capability. The FPGA contains over 1,300K LUTs. The 16 GB of HBM2 has a total bandwidth of 460 GB/s.
The Alveo family is supported by Xilinx's Vitis unified software platform (Fig. 3). The module system allows developers with a wide range of expertise to take advantage of these FPGA-based systems. FPGA developers can get down to the details of programming the FPGA through software developers who don't even care that an FPGA is underneath the system. The collection of accelerated libraries and APIs provide a way to utilize the system without the need to deal with the FPGA directly.
Vitis supports the major machine-learning frameworks like TensorFlow, Caffe, and PyTorch. The APIs support languages such as C, C++ and Python.
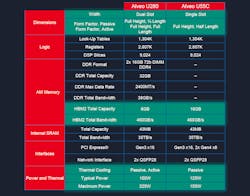
The board is designed to handle high-performance-computing (HPC) loads. The Alveo U55C delivers significantly more performance in a smaller package using less power than its predecessor, the Alveo U280 (Fig. 4).
The U55C will have a major impact on the capacity and requirements in the cloud while providing significant performance benefits for applications ranging from machine learning to multimedia transformations.