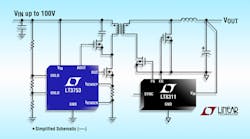
Synchronous Forward Controller Shrinks 25- To 400-W Power-Supply Footprints
A programmable volt-second clamp built into Linear Technology’s LT3753 primary-side, current-mode, pulse-width-modulation (PWM) controller allows for transformer and MOSFET optimization, resulting in reduced solution size. When the clamp is set above the converter’s natural duty cycle, it provides a duty-cycle guardrail to limit primary switch reset voltage and prevent transformer saturation during load transients. It also limits maximum VOUT if the optocoupler path breaks open, or it will define VOUT in applications without an optocoupler. Output voltage regulates to ±5% without the use of an optocoupler. With an opto, it’s possible to realize ±1.5% regulation. The LT3753 operates over an input-voltage range of 8.5 to 100 V, delivers up to 95% efficiency, and targets power levels up to 400 W. The device sends a control signal via a pulse transformer to a secondary-side MOSFET driver for the synchronous rectification timing. It integrates a voltage error amplifier for non-isolated high step-down ratio applications. Programmable operating switching frequency ranges from 100 to 500 kHz. Synchronization to an external clock enables use of a wide range of output inductor values and transformer sizes. All versions of the LT3753 come in TSSOP-38 packaging with several pins removed for high-voltage spacing.