Members Only Content
Using PoL DC-DCs to Solve Voltage Accuracy, Efficiency, Latency Issues (.PDF Download)
Aug. 11, 2021
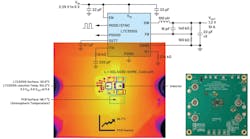
Proximity to power. It’s one of the best ways to improve voltage accuracy, efficiency, and the dynamic response of a power rail. A point-of-load (PoL) converter is a power-supply dc-dc converter placed as close to the load as possible to achieve proximity to power.
Applications that benefit from PoL converters include high-performance CPUs, SoCs, and FPGAs—all of which require ever-increasing power levels. In automotive applications, for example, the number of sensors used for an advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS)—such as those in radar, LiDAR, and vision systems—is steadily multiplying. Thus, faster data processing (more power) is needed to detect and track surrounding objects with minimal latency.
Comments
Comments