Researchers from institutions including Lund University in Sweden have taken a step closer to producing solar fuel using artificial photosynthesis. In a new study, they have successfully tracked the electrons’ rapid transit through a light-converting molecule
The current study aims to find a way to make fuel from water using sunlight, which is the basic principle of photosynthesis – plants converting water and carbon dioxide to energy rich molecules using sunlight. Researchers worldwide are attempting to borrow ideas from photosynthesis in order to find a way to produce solar fuel artificially.
“Our study shows how it is possible to construct a molecule in which the conversion of light to chemical energy happens so fast that no energy is lost as heat. This means that all the energy in the light is stored in a molecule as chemical energy”, said Villy Sundström, Professor of Chemical Physics at Lund University.
Up to now, solar energy is harnessed in solar cells and solar thermal collectors. Solar cells convert solar energy to electricity and solar thermal collectors convert solar energy to heat. However, different technology is require to produce solar fuel. The idea is that solar light can be used to extract electrons from water and use them to convert light energy to energy rich molecules, which are the constituent of the solar fuel.
“A device that can do this – a solar fuel cell – is a complicated machine with light-collecting molecules and catalysts”, said Villy Sundström.
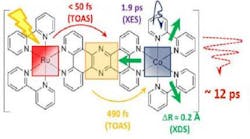
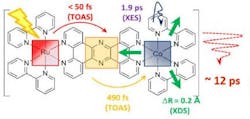
In the present study, Professor Sundström and his colleagues have developed and studied a special molecule that can serve as a model for the type of chemical reactions that can be employed in a solar fuel cell. The molecule comprises two metal centers, one that collects the light, and another that imitates the catalyst where the solar fuel is produced. The researchers have managed to track the path of the electrons through the molecule in great detail. They measured the time it took for an electron to cross the bridge between the two metal atoms in the molecule. It takes half a picosecond, or half a trillionth of a second.
“In everyday terms, this means that the electron flies through the molecule at a speed of around four kilometres a second, which is over ten times the speed of sound”, said Villy Sundström.
The researchers were surprised by the high speed. Another surprising discovery was that the speed appears to be highly dependent on the type of bridge between the atoms. In this study, the speed was 100 times higher than with another type of bridge tested.
“This is the first time anyone has managed to track such a complex and rapid reaction and to distinguish all the stages of the reaction”, said Villy Sundström about the study, which has been published in the journal Nature Communications.