This Week in PowerBites: Electricity is in the Air
This article is part of the Power Management Series: This Week in PowerBites
Long-Range Wireless Charging May No Longer be Science Fiction
Nikola Tesla's dream of long-range wireless power transmission took a small step toward reality when Motorola announced an initiative to equip some of its next-generation smartphones with over-the-air wireless-charging capabilities. Working in partnership with GuRu Wireless, Motorola intends to use GuRu's proprietary millimeter-wave (mmWave) technology to create the first generation of smartphones capable of receiving power over-the-air up to a meter from the wireless transmitter.
GuRu brings a broad portfolio of technologies to the project, including the proprietary Smart RF Lensing technology involving integrated circuits and modules that was created to enable safe, effective, and customizable transmission of power over-the-air. Florian Bohn, CEO and co-founder of GuRu, said that its wireless solution can be used as a charging hub or a power source in many settings where access to an energy source is needed. It’s easy to install, safe, and sophisticated enough to find and adjust for various power levels to sync with the needs of any device.
Bohn also hinted that smartphones may only be the first of several applications GuRu Wireless will be tackling with Motorola. “We are excited to join forces with an industry leader whose goal is to improve the consumer experience. Together, we will introduce true mobility for portable smart devices and IoT sensors.”
For more information, visit https://guru.inc/technology-2/.
Wireless Power All Grown Up—and No Microwaves Involved!
Eggtronic, the Modena-based R&D firm that brought you the Qi wireless-charging system, has rolled out something a little more powerful this time. And it may change the way we power laptops, displays, and almost any other electric product that operates on a flat surface.
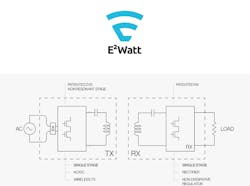
The E2WATT wireless platform is a new ac power-transfer technology that works across much longer distances (up to 40 mm) and delivers up to 300 W or more at efficiencies associated with premium wired ac adapters. The wireless technology is powered directly from ac mains, without the cost and complexity of an external power supply. It uses a single-stage hybrid design that minimizes losses compared with conventional double-stage wireless technologies to deliver significantly increased peak efficiencies of up to 95%.
Applications include wireless laptops, TVs, sound systems, home and kitchen appliances, and most other higher-power electric and electronic products. Eggtronic even hinted that variants of the low-loss wireless charging technology may find applications in electric vehicles.
The platform's technology is licensable and based on a flexible reference design built around commercially available gallium-nitride (GaN) power ICs, a PWM-capable microcontroller, and Eggtronic's custom ASIC that implements its unique power-transfer technique. Much of the technology behind the technique is proprietary, as evidenced by the redacted schematic they used to brief the trade press. And while Eggtronic's promotional video contains even less technical information than the schematic, it's lots of fun to watch and does provide a look at what the technology might make possible:
Thankfully, Igor Spinella, CEO and founder of Eggtronic, generously shared a few insights during a recent interview with Electronic Design. During our chat, he explained that some of E2WATT's high efficiency comes from its use of high-speed GaN semiconductors from Navitas Semiconductor, which enable the inductive coupling circuits in the transmitter and receiver to be precisely switched to minimize device losses.
Spinella explained that, to further improve efficiency, the receiver side monitors its load's power demand and uses a digital backchannel to adjust the transmitter's frequency and pulse width to only transmit the required power. It also incorporates Microchip Technology’s flexible dsPIC33 microcontroller with a powerful DSP core, high-speed analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), and high-resolution pulse-width modulators (PWMs) to help Eggtronic's unique system architecture achieve its increased z-distance charging.
Servo Controller/Driver Module Simplifies Robotic and Automation Dev, Cuts Power Losses by 75%
Trinamic Motion Control, a division of Maxim Integrated, has introduced the industry's smallest and lowest-power single-axis servo controller/driver module with integrated motion control. The TMCM-1321 module provides intelligent motion control for two-phase bipolar stepper motors that enables robotic and automation equipment to optimize speed and synchronize multiple axes for quicker throughput.
The TMCM-1321 module integrates a powerful MCU, digital ABN inputs, an on-board magnetic encoder, and digital inputs for an optical encoder to simplify servo control and support advanced motion-control algorithms. The module's controller firmware can perform linear ramping, Trinamic SixPoint ramping, as well as advanced S-shaped ramping to speed effective transfer time. The company’s closed-loop technology utilizes direct feedback to automatically reduce power loss by 75%.
Together with an RS-485 interface and Trinamic’s integrated development environment, the TMCM-1321 module simplifies design and reduces stepper-motor size by more than 3X. Boasting a footprint of only 784 mm2, it enables the industry's most compact motion-control solution in its class.
The TMCM-1321 module is available now for $119.40 each through Trinamic authorized distributors. For further details about the TMCM-1321, visit http://bit.ly/TMCM-1321
Flyback-Switcher ICs for a New Class of Mobile Charging Devices
Power Integrations recently unveiled the InnoSwitch4-CZ family of high frequency, zero voltage switching (ZVS) flyback-switcher ICs. These devices incorporate a 750-V switch, primary and secondary controllers, ClampZero interface, synchronous rectification, and safety-rated feedback in a single, compact InSOP-24D package. Together, they enable a class of ultra-compact chargers that offer new levels of power density, reliability, and value for phones, tablets, and laptops.
The switcher ICs can handle steady-state switching frequency of up to 140 kHz, which minimizes transformer size and further increases power density. They support variable-frequency asymmetrical control of the active clamp with intelligent zero-voltage switching. This enables both discontinuous and continuous conduction modes of operation, greatly enhancing design flexibility and maximizing efficiency across the entire operating envelope.
When paired with Power Integrations' ClampZero solution, the InnoSwitch4-CZ provides up to 95% efficiency and maintains very high efficiency across variations in line voltage, system load, and output voltage. The new flyback-switcher ICs also enable exceptional CV/CC accuracy, independent of external components, and consume less than 30 mW no-load including line-sensing safety and protection features.
Targeting high-efficiency compact USB PD adapters, high-density flyback designs up to 110 W, and high-efficiency CV/CC power supplies, InnoSwitch4-CZ ICs provide variable output voltage and constant current profiles. Devices are fully protected, featuring auto-restart or latching fault response for output overvoltage and undervoltage protection, multiple output undervoltage fault thresholds, and latching or hysteretic primary overtemperature protection.
The new InnoSwitch4-CZ ICs are priced at $3.85 per unit in 10,000-unit quantities. Additional details on the architecture, operation, and application of the InnoSwitch4-CZand ClampZero devices can be found in a no-nonsense technical video at this link.
Tiny-Footprint, Ultra-Low-IQ PMIC Targets Wireless SoCs and Other Products
The first power-management IC (PMIC) from Nordic Semiconductor, the “nPM1100,” combines a USB-compatible input regulator (with overvoltage protection), a 400-mA battery charger, and a 150-mA dc-dc step-down (“buck”) voltage regulator in a 2.075- × 2.075-mm wafer-level chip-scale package (WLCSP). The complete power-management solution takes up as little as 23 mm2 of PCB area, including passive components, making it ideal for advanced wearables, connected medical devices, and other space-constrained applications.
The PMIC was designed to provide reliable power, stable operation, and maximum battery life for Nordic’s nRF52 and nRF53 Series multiprotocol systems-on-chip (SoCs). It supports USB standard downstream port (SDP) from either a 4.1- to 6.6-V USB input or from a 2.3- to 4.35-V connected battery input; charging downstream port (CDP); and dedicated charger port (DCP) detection. The input regulator includes overvoltage protection for transient voltage spikes up to 20 V. In addition, the nPM1100 can be used as a generic PMIC for any application using rechargeable lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries.
The product’s highly efficient dc-dc buck voltage regulator can supply up to 500 mA at more than 90% efficiency down to below 100-µA load current. It takes its power from the input system regulator and provides up to 150-mA current at a selectable 1.8-, 2.0-, 2.7-, or 3.0-V regulated output voltage. The regulator features soft startup and automatic transition between hysteretic and pulse-width-modulation (PWM) modes, plus a forced PWM mode for the lowest possible noise operation. The nPM1100 also features an ultra-low quiescent current (IQ) of 700 nA (typ.), which can be further reduced to 470 nA in “ship mode” for transit.
The PMIC’s JEITA-compliant battery charger will charge the application’s Li-ion/Li-Po battery with a resistor-selectable charge current from 20 to 400 mA and a selectable termination voltage of 4.1 or 4.2V across product’s operating temperature range of −40 to 85˚C.
The nPM1100 is in volume production and samples are available now. Nordic's PMIC is supported by the nPM1100 Evaluation Kit, which allows designers to test the nPM1100 PMIC’s capabilities with existing applications without custom hardware. Additional information on the device can be found at the nPM1100 product page.
Nordic also is presenting a webinar on June 9, 2021—intended to familiarize engineers and others with the nPM1100—click here to register.
High-Temp, Hi-Rel, Power DC-Link Film Capacitor for Automotive, Green-Energy Apps
KEMET’s new C4AK high temperature, power film dc-link capacitor is designed for continuous operation up to 1,000 hours at 135°C. The C4AK series joins the C4AU (harsh environment) and C4AQ-P (125°C) families, which offer higher capacitance density, dc voltage, and dc ripple current capabilities with an extended operational lifetime at high temperatures in harsh environments.
These metallized film capacitors handle the high frequency and high current often found in automotive, green, and industrial applications, particularly those involving wide-bandgap semiconductors. This includes dc filtering and dc-link in solar, fuel cells, inverters, energy-storage systems, automotive (Bi) on-board chargers, wireless power transfer (WPT), dc-dc, heaters, and welding equipment.
The dc-link C4AK's enhanced performance design provides a superior alternative to previous hi-rel capacitor solutions. It features a radial box style for PCB mounting, miniaturization, low profile, two to four leads, and requires fewer capacitors in parallel to meet the required peak and ripple current.
The device also works reliably in conditions that are even more extreme than required by the AEC-Q200 automotive standard for film technology in severe humidity/temperature conditions. Compared to competitor’s technologies, the C4AK series offers higher performance with a lifetime of 4,000 hours at 125°C and 1,000 hours at 135°C in harsh environmental conditions.
The C4AK power film capacitor is available now. Additional information is available at https://www.kemet.com/en/us/new-products.html
40-V MOSFETs Bring Low RDS(on) , High Power Density, and More to Automotive, Industrial Apps
A new family of 0.55 mΩ RDS(on) 40 V power MOSFETs developed by Nexperia targets automotive (BUK7S0R5-40H) and industrial (PSMNR55-40SSH) applications. Housed in an 8- × 8-mm LFPAK88 high-reliability copper clip package, the devices’ extremely low on-resistance enables them to deliver power densities that are 50X higher than traditional D2PAK devices. The devices, available in both automotive and industrial grades, also offer improved performance in both avalanche and linear mode, providing increased ruggedness and reliability.
Furthermore, the power MOSFETs feature excellent linear-mode/safe-operating-area (SOA) characteristics for safe and reliable switching at high-current conditions. Their SOA at 1-ms, 20-VDS operating conditions is 35 A due to a combination of silicon and package, while at 10 ms, 20 VDS, where the package dominates, SOA is 17 A. These figures are 1.5X to 2X better than the competition.
According to the company, the devices offer the best single pulse avalanche rating (EAS) at 2.3 J and very strong ID current rating of 500 A, which—unlike some competing devices—is a measured rather than theoretical limit.
The new MOSFETs’ size and performance benefits can enable designers to simplify and cost-optimize existing designs by replacing two paralleled older components with a single LFPAK88. The automotive-grade BUK7S0R5-40H parts greatly exceed the reliability performance requirements of the AEC-Q101 automotive standard, making them a good choice for critical systems, such as braking, power steering, reverse battery protection, e-fuse, dc-dc converter, and motor-control applications.
The industrial-rated PSMNR55-40SSH MOSFETs zero in on applications such as battery isolation, current limiting, e-fuses, motor control, synchronous rectification, and load switches in power tools, appliances, fans, and e-bikes, scooters, and wheelchairs.
For more information, including product specs and datasheets, visit www.nexperia.com/lfpak88. To learn more about the unique construction of the LFPAK88 copper-clip package, watch https://bit.ly/3yd47xQ.
Electric Air Racing Anyone?
There's literally electricity in the air with the recent news that the Air Race E organization will be announcing a venue for the first international electric airplane race. Unlike the supersized drones covered by PowerBites last year, which were being developed by Airspeeder for a long-promised and still yet-to-be announced racing series, Air Race E seems to be on track to deliver the goods.
This is largely to the series being an offshoot of an existing, and very popular motorsport format known as formula one air racing. Like its terrestrial counterpart, these races involve several competitors vying for the lead in a closed circuit. However, in this case, they fly around six pylons, just meters above the ground, and at speeds that their wheeled counterparts can only dream of.
Eventually, the league intends to field three classes of e-racers, beginning with "Performance Class" airplanes. This class of airplanes will be modeled after the existing ICE-powered formula one air racers and use a standard electric powertrain, with some provisions for allowable modifications.
Air Race E says that a prototype Performance Class airplane is under construction with the goal of using it to help shape the model and rules for Air Race E, which is set to launch its inaugural series in 2022. The prototype uses the airframe of an existing petrol-powered Air Race 1 that’s currently being retrofitted with a new integrated “plug and play” electric motor, battery, and power electronics system. The new propulsion system development and the retrofit are taking place in workshops at the University of Nottingham, who has partnered with Air Race E.
For more information, visit the Air Race E website.
Read more from the Power Management Series: This Week in PowerBites