This Week in PowerBites: Solid-State Caps and Solar-Energy Fuses
This article is part of the This Week in PowerBites Library Series.
Hopeful Sci-Fi Makes for Great Summer Reading for Engineers
With the shadow of the pandemic almost behind us, enjoying a "normal" summer feels like a rare privilege. I intend to spend much of this precious time (carefully) reconnecting with friends and exploring the wilds of New Jersey with my wife Catherine. Nevertheless, I'm still making lots of room for healthy stretches of what's referred to as "Summer Reading." Few things can make the stresses of my everyday life dissolve more gently than relaxing with an adult beverage and an engrossing novel.
While I enjoy the occasional trashy romance, murder mystery, or spy thriller, there's nothing like some well-written science fiction to satisfy my engineer's sensibilities—especially if things turn out for the better at the end. The problem is that hopeful sci-fi seems to be as scarce as vacuum tubes these days, as they both seem to be much-beloved relics of a bygone era.
But hope is still on the menu, thanks to authors like Richard Bowers, Ursula K. Le Guin, Greg Baer, and others who give us stories about futures worth living. We’re even blessed with folks like Kim Stanley Robinson, whose stories contain imaginative, believable roadmaps on how we can get there. It's no wonder then why Robinson's latest work, “The Ministry For The Future,” occupies the top slot in my Audible listening list this summer.
Set in the very near future, Robinson paints a disturbingly accurate picture of how climate change will unfold over the next 10-20 years without any further efforts to mitigate it. In this future, however, the world is galvanized into action as the death, famine, and economic collapse begins to spread beyond the confines of "developing nations" and undertakes an ambitious plan to drag humanity back from the edge of oblivion.
Stay tuned for my upcoming full review of the book on www.electronicdesign.com.
Meeting the Design Challenges Created by the EU's USB-C Harmonization Directive
Until now, many companies would design and ship a specific charger for their product. In some cases, they even used non-standard barrel-style jacks to ensure consumers would only use the charger they conceived. The European initiative will suddenly require that one charger must work with a wide range of devices, requiring engineers to account for more edge cases, faulty sink systems, etc.
To help designers better understand these challenges, STMicroelectronics has prepared an informative blog post on using its TCPP02-M18 to protect USB Type-C ports against the overcurrent and overvoltage conditions specified in the EU directive. Besides the obligatory product pitch, the post covers important topics that include:
- New Challenges from Harmonization
- What Makes Source Protection Special?
- VBUS Protection
- CC and VCONN Protection
You can check it out at https://blog.st.com/tcpp02-m18/.
2nd-Gen Silicon Capacitor Arrays Deliver Higher Density and Performance
Empower Semiconductor expanded its E-CAP family of silicon capacitors with a new series that offers a 2X increase in density and improved performance.
Designed an advanced trench capacitor technology (originally derived from VFET structures), the latest E-CAP solutions offer densities of 1.1 µF/mm2. That’s more than 5X the capacitance of a comparably sized multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC) and more than twice the density of alternative silicon capacitor technologies, according to the company.
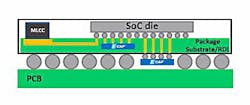
E-CAP technology makes it possible to produce solid-state capacitor arrays. The improved E-CAP devices also offer improved equivalent-series-inductance (ESL) and equivalent-series-resistance (ESR) characteristics. They dramatically reduce parasitic effects that can otherwise degrade an application's performance.
Multiple, matched capacitance values from 75 pF to 5 µF (@2 V) can be integrated into a single die to create custom integrated capacitor arrays, while form factors may be customized for the space and height limitations of a particular application.
Packaging options based on bumps, pads, and pillars allow designers to choose the best solution based on specific system constraints, some with thickness levels of below 50 µm in overall height. As a result, E-CAPs can be embedded, or attached to the bottom, of high-powered SoC devices' packages, where their small size and versatile packaging/mounting options enable them to be located much closer than would be possible with a larger MLCC. Empower's 1st-generation E-CAP technology also is available for applications requiring operating voltages of up to 4 V.
Using E-CAP arrays, designers are able to combine all non-bulk, high-frequency decoupling capacitors into a single die to dramatically reduce component count, bill-of-materials (BOM) cost, and potential points of failure. Empower says that although the E-CAPs have lower nominal capacitance, their superior frequency response and ESL over MLCCs results in lower impedance at high frequencies.
In addition, unlike MLCCs where multiple devices are needed to account for derating from voltage, temperature, and age, E-CAP requires no ac or dc bias derating while all other derating requirements are negligible. This eliminates the need to “over specify” capacitance requirements to account for derating.
VDD Tech's dV/dt sensing, blanking, and refresh technologies offer a "powerful" combination of very-high-voltage-isolation capability and high-frequency operation that provides 5X to 10X higher dV/dt immunity than legacy silicon. Likewise, VDD's structures offer low isolation-capacitance (<0.5 pF) and robust modulation that can be used to provide low-jitter digital-communication for isolated-driver control and analog-sensing feedback.
These advanced digital-isolation techniques and other capabilities should help Navitas give designers solutions that deliver size, weight, and system-cost improvements for their high-power applications in consumer, motor-drive, solar, data-center, and EV markets.
Smart BMICs Offer Excellent Measurement Performance, Help Optimize Battery Life
Infineon Technologies' new family of battery-management ICs (BMICs) helps to optimize solutions for battery-cell monitoring and balancing. The TLE9012DQU and TLE9015DQU combine excellent measurement performance with the highest application robustness in a system-level solution for battery modules, cell-to-pack and cell-to-car battery topologies, according to the company.
Both BMICs are ASIL-D- and ISO 26262-compliant, making them suitable for use in safety-critical applications, including mild hybrid electric vehicles (MHEVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and battery-powered electric vehicles (BEVs), as well as electric two- and three-wheelers.
The TLE9012DQU multichannel battery-monitoring and -balancing system IC can perform highly accurate voltage measurements for state-of-charge (SoC) and state-of-health (SoH) calculation—the key requirements for any battery management system. The ASIL-D-compliant device, designed for lithium-ion battery packs, can be controlled directly by a microcontroller via UART or via an isolated UART interface with the new TLE9015DQU iso-UART transceiver IC.
The design of the TLE9012DQU is based on a parallel analog-to-digital converter (ADC) architecture that enables high accuracy throughout its service life without the need for external compensation components. It uses 16-bit DS ADC technology to deliver excellent noise rejection through high internal oversampling, and advanced sync-on-sample at less than 10 µs across an entire battery pack.
The TLE9015DQU is a battery-monitoring transceiver IC designed for connecting several TLE9012DQU devices in a daisy chain inside a Li-ion battery. It uses its two UART and ISO-UART interface pairs to support ring communication for improved system cost efficiency. By integrating an error management unit that includes several inputs and outputs programmable on each TLE9012DQU, the module also enables bidirectional information flow.
Furthermore, the BMICs are optimized to work together with Infineon's AURIX family of microcontrollers and functional-safety-capable power-management ICs. They can be combined to provide a full solution set of voltage- and temperature-sensing capabilities, as well as balancing and communication across many types of battery-pack architectures.
Availability
The TLE9012DQU and TLE9015DQU are both available for use in production designs. More information is available at https://www.infineon.com/bmsic.
Rugged 1,000-V AC/DC Common-Mode Choke Solution for EMI Suppression
The new SCF-XV series of AEC-Q200-qualified common-mode chokes from KEMET is intended to help meet the growing need for high-reliability, high-voltage (up to 1,000-V ac/dc) filtering in automotive and other demanding applications (robotics, medical, high-voltage power supplies, etc.). With rated current ranges from 5 to 35 A, and DCR from 0.65 to 40.3 mΩ, the series supports an operating temperature of −40 to +150°C.
The chokes' toroidal coils are designed with nanocrystalline metal cores that support higher flux densities, enabling more compact form factors and smaller footprints. They’re available in two different layouts (vertical/horizontal) and three different outer core diameters (19/25/29 mm).
The 1,000-V ac/dc rating and AEC-Q200 qualification offered by the SCF-XV series, and their companion SCR-XV and SCT-XV components, makes them well-suited for use in EV applications where many manufacturers are moving to 800-V battery packs. With its space-saving characteristics, this series also addresses the trend of miniaturization and operation in harsh environmental conditions. Applications include onboard chargers for EVs/PHEVs, E-compressors, wireless-charging systems with 85 kHz, medium power drives for power steering, air conditioning, and mild-hybrid 4-V systems. The SCF-XV series is available immediately via KEMET distributors. To learn more about its capabilities and applications, visit https://www.kemet.com/en/us/new-products.html.
UL 248-14-Compliant High-Power Fuses Offer Current-Event Protection, Wide Temp Range
Bourns Inc. added three new series to its POWrFuse High-Power Fuse product family. The POWrFuse Model PF-G (63 A), PF-J, and PF-H series are specifically designed to meet the requirements of UL 248-14, while Model PF-G (90 A) is designed to meet the requirements of both the UL 248-14 and the UL 248-1 standards. These capabilities help protect systems from extreme ambient temperatures and fault current events, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, including home appliances and industrial products.
These devices join the POWrFuse PF-E and PF-H (gPV) series, introduced earlier this year, which are designed specifically to help protect solar photovoltaic power systems known to operate under extreme ambient temperatures, and high-cycling and low-level fault current conditions.
Key specifications include:
- The Model PF-G series is rated for 500-V ac (90 A) and 600-V ac (63 A) ratings, and up to a 2-kA interrupting rating.
- The POWrFuse PF-H series (Ind) features up to a 12-A current rating with up to a 100-kA interrupting rating and is available in ferrule or PCB mounting options.
- The POWrFuse PF-J series has products available with 30- to 70-A/500-V ac ratings and up to a 2-kA interrupting rating. All three new series deliver an operating temperature range of −55 to +125°C and offer fast-acting protection under fault current, low resistance, and power loss.
- The POWrFuse PF-E series is designed to the UL 248-19 (Class gPV) photovoltaic fuse standard and offers 1000-V dc voltage, power ratings from 15 to 30 A, and up to a 20-kA interrupting rating.
- The POWrFuse PF-H (gPV) series is designed to the UL 248-19 and IEC 60269-6 (Class gPV) photovoltaic fuse standards and offers 600-V dc/ac voltage, power ratings from 15 to 30 A, and up to a 150-kA interrupting rating.
Ferrule and PCB mounting options are available for both series.
The model PF-E, PF-H (gPV), PF-G, PF-J, and PF-H (Ind) series, all available now, are RoHS-compliant and halogen-free. For more detailed product series information, visit www.bourns.com/products/fuses/powrfuse-high-power-fuses
40-V MOSFETs Use Oxide-Filled Trench Process for Higher Efficiency, Lower Noise
The STL320N4LF8 and STL325N4LF8AG 40-V MOSFETs developed by STMicroelectronics offer reduced on-resistance and switching loss, plus optimized body-diode properties to save energy and ensure low noise in power-conversion, motor-control, and power-distribution applications. The new N-channel enhancement-mode MOSFETs leverage ST's latest-generation STripFET F8 oxide-filled trench technology to achieve superior figures of merit.
Both devices feature a maximum on-resistance (RDS(on)) of 0.8 mΩ and 0.75 mΩ, respectively, and gate-source voltage (VGS) of 10 V. The MOSFETs efficient RDS(on) per die area allows for a space-saving and thermally efficient PowerFLAT 5x6 package.
ST’s advanced STripFET F8 technology also accelerates switching speed through low device capacitances that minimize dynamic parameters, such as gate-drain charge, for improved system efficiency. Designers can select switching frequency in the range from 600 kHz to 1 MHz, permitting smaller capacitive and magnetic components to save circuit size and BOM, as well as increase the power density of the final application.
A proper output capacitance and associated ESR can be selected to prevent spikes in the drain-source voltage and ensure shorter damping oscillation time at turn off. With this, and the body diode’s soft-recovery characteristic, the STL320N4LF8 and STL325N4LF8AG emit extremely low electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to other similar devices in the market, according to the company. In addition, the diode has low reverse-recovery charge that minimizes energy losses in hard-switching topologies.
The devices' gate threshold voltage (VGS(th)) is tightly controlled to ensure a narrow spread across devices in applications requiring multiple MOSFETs connected in parallel for higher currents. They also offer rugged short-circuit resilience, withstanding up to 1000 A (pulses shorter than 10 µs).
Well-suited for battery-powered products and applications in computing, telecom, lighting, and general power conversion, the STL320N4LF8 and STL325N4LF8AG are the first industrial-qualified and AEC-Q101-qualified STPOWER STripFET F8 MOSFET devices, respectively.
The MOSFETs are in mass production now, priced from $1.29 and $1.40, respectively, for orders of 1,000 units. For further information, visit www.st.com/f8-stripfet.
Read more articles in the This Week in PowerBites Library Series.