How Incident and Maintenance Documentation Saves More than Lives Using IEC61508
Our world is moving at a rapid pace and so is automation across the spectrum. Everything from self-driving cars, personal recreational drones and robotic surgery to automated amusement rides. What do these advanced control technologies have in common? A failure can result in serious harm or death for the passenger, patient, or amusement park attendee without proper documentation.
Functional Safety with IEC61508
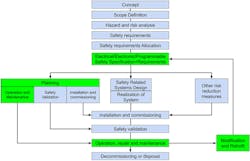
A holistic approach to design safety is required to ensure that electrical, control, and sensor systems can’t fall into a dangerous failed state. IEC61508 was developed in the early 2000s to address this issue. However, it was significantly updated in 2010 to include the full product’s life and management. This standard ensures that product management extends beyond the specification and design stage, but it also deals with commissioning, testing, operations, and maintenance (see figure).
Holistic design aims to eliminate flaws, although it’s possible that systemic design deficiencies don’t appear until months or even years after operation. They can be caught by extending the design to a cradle-to-grave approach, where every interface of the machine is recorded and retained as part of the product’s documentation.
Documentation is a pain point for designers, engineers, and machine operators across many sectors. In the attractions industry, it’s critical to maintain safe operations due to the public's exposure to risk. Does that mean every repair done to an automated go-kart needs to be recorded? How much liability does the park owner inherit by documenting the bulk of their maintenance issues?
Those are commonly asked questions that can hinder functional safety assessments when presented with misinformation. It also limits the ability to attain a root cause for systemic failures when trends and repeat events can’t be traced.
What’s the Correlation Between Operator Liability and Functional Safety?
Functional safety allows for a comprehensive overview of a system and its subcomponents to highlight areas of potential fault. It also indicates when to retire, service, or replace aging equipment.
If maintenance records are poorly contrived, it opens the operator to liability concerns should an event occur. The worst-case scenario could involve severe injury, loss of life, and financial and reputational impacts. To mitigate risk, functional safety engineers are hired to create a process that outlines the product’s entire lifecycle to develop a maintenance plan for longevity and to reduce the chance of a catastrophic failure.
Some believe that not keeping records can minimize risk to the organization. It’s willful ignorance to assume such, as the liability may shift from the manufacturer to the owner if poor record-keeping demonstrates negligence. It’s best to hire a consultant to review the records and process them for reporting purposes. For example, define what’s a “near miss” and when a maintenance record should be made.
Tragedy in Queensland
The importance of good documentation can’t be understated. In 2016, an amusement park based in Queensland, Australia faced tragedy when four attendees lost their lives on a raft-based water ride after two hydro pumps failed. The sudden drop in water levels caused the ride-goers to be ejected from their raft, which resulted in fatal injuries.
From a controls and monitoring perspective, the system fell into an undetectable dangerous state. Could this dangerous failed state have been identified and fortified if a risk assessment was completed? Perhaps adding multiple sensors or including a maintenance provision for aging components could have prevented this if a proper risk assessment was conducted, properly reviewed, and documented.
Brisbane Magistrate Court investigated the incident and determined that the owners and operators witnessed a systematic failure in ensuring all aspects of safety. The world-class amusement park presented no evidence of conducting a safety risk assessment in over three decades of operation. An incident of this magnitude is avoidable and can’t be left to chance. The lack of documentation didn’t provide the operators with enough information to understand the water pumps’ integrity and when to service them.
An example of a functional safety process for a machine can be seen in the figure. The most relevant part for the park operator is highlighted in green for the O+M planning section: operation, repair, and maintenance procedures. The park operator may require more than the supplier’s manual to ensure safe operation of the ride.
A Safety-Critical Process
Functional safety isn’t only restricted to amusement parks—it’s pertinent across all industry sectors. Quality assurance for safety-critical systems demands constant monitoring, reporting, and maintenance. Good documentation will remove the guesswork for owners and allow for more accurate decision-making based on historical data and trends.
Dr. Michael Wrinch, P.Eng., is President of Hedgehog Technologies.