Bluetooth Builds Up with Broadcast and Distance Features
What you’ll learn:
- What is Bluetooth Auracast broadcasting?
- What is Bluetooth Channel Sounding?
The Bluetooth SIG showed off two new Bluetooth features at this year’s Consumer Electronics Show, including Auracast and Channel Sounding. I spoke with Dave Hollander, Bluetooth SIG Vice President of Marketing, and Damon Barnes, Bluetooth SIG Director of Technical Marketing, about these new features (watch the video above).
Auracast Brings Broadcasting to Bluetooth
In the past, Bluetooth was primarily a personal area network (PAN). A central device like a smartphone or PC could exchange audio with devices like microphones and headphones as well as I/O devices such as keyboards and mice.
Auracast targets a scenario where audio will be streamed to more than one Bluetooth audio device. This is akin to radio broadcasts or more similar to Wi-Fi connections to multiple devices like Wi-Fi speakers. Auracast broadcast nodes tend to be fixed and have a more robust power source, allowing for a higher-power transmitter that provides longer range operation.
>>Check out our video coverage of CES 2025, and visit this TechXchange for similar articles and videos on the technology
There are a number of use cases, such as providing broadcasts of meetings for each room in a museum, or in auditoriums. The latter is handy for those with hearing aids as well as those with earbuds and headphones. It could be very useful in noisy environments, supported by augmented-reality (AR) glasses with audio output.
Bluetooth Channel Sounding for Distance Measurement
Bluetooth Channel Sounding tales on an entirely different application—it can provide the distance between a pair of Bluetooth devices. The technology uses two different mechanisms.
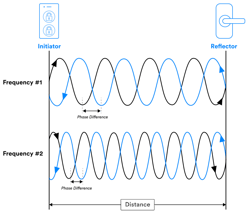
Phased-based ranging (PBR) delivers precise measurements by checking the phase difference of reflected radio waves (Fig. 1). There’s an initiator and a reflector, with the initiator sending the initial signal. Multiple frequencies are used to improve the accuracy.
A secondary approach leverages round trip time (RTT) when sending packets (Fig. 2). It can be used to mitigate man-in-the-middle (MITM) security attacks. Encrypted data packets prevent spoofing by an attacker. The initiator determines the distance based on the RTT.
Bluetooth Position Information
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) supports angle-of-arrival (AoA) and angle-of-departure (AoD) methods of signal direction estimation, although not all devices have such support. At this point, channel sounding can provide distance measurements with about 10-cm accuracy, which is sufficient to determine if a device is in a room. It doesn’t include an angular component without the AoA or AoD support.
Position could also be determined using triangulation between multiple devices, but this is likely only useful for a small set of applications. Though other wireless positioning systems are available, the channel-sounding feature has the advantage of using existing Bluetooth support.
>>Check out our video coverage of CES 2025, and visit this TechXchange for similar articles and videos on the technology
About the Author
William G. Wong
Senior Content Director - Electronic Design and Microwaves & RF
I am Editor of Electronic Design focusing on embedded, software, and systems. As Senior Content Director, I also manage Microwaves & RF and I work with a great team of editors to provide engineers, programmers, developers and technical managers with interesting and useful articles and videos on a regular basis. Check out our free newsletters to see the latest content.
You can send press releases for new products for possible coverage on the website. I am also interested in receiving contributed articles for publishing on our website. Use our template and send to me along with a signed release form.
Check out my blog, AltEmbedded on Electronic Design, as well as his latest articles on this site that are listed below.
You can visit my social media via these links:
- AltEmbedded on Electronic Design
- Bill Wong on Facebook
- @AltEmbedded on Twitter
- Bill Wong on LinkedIn
I earned a Bachelor of Electrical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and a Masters in Computer Science from Rutgers University. I still do a bit of programming using everything from C and C++ to Rust and Ada/SPARK. I do a bit of PHP programming for Drupal websites. I have posted a few Drupal modules.
I still get a hand on software and electronic hardware. Some of this can be found on our Kit Close-Up video series. You can also see me on many of our TechXchange Talk videos. I am interested in a range of projects from robotics to artificial intelligence.