Intelligent Power Device Meets Space-Challenged BLDC Motor-Drive Needs
Advanced and sophisticated control of all types of motors, and especially brushless DC (BLDC) types, has been receiving lots of attention and support in recent years. This makes sense, as advanced control algorithms coupled with the appropriate drivers, switching devices, and advanced motor designs can result in greatly improved dynamic performance, power savings, and many other benefits.
As a result, the classic induction motor is being “pushed aside.” Now we’re seeing BLDC motors used across a wide range of consumer end-products ranging from small countertop appliances to mid- and larger-size ones, such as clothes washers and dryers, air conditioners, heat pumps, and similar applications.
Higher-Rated Mini Intelligent Power Device
Addressing the need for BLDC motor drive in the small-appliance area, Toshiba Electronics released a small intelligent power device (IPD) for space-constrained BLDC motor-drive applications such as air conditioners, air purifiers, and pumps (exactly how you define the difference between “smart” and “intelligent” devices is a subject for another time and place).
The new IPD, designated TPD4165K, has an increased maximum output current of 3 A compared to the 2-A rating of Toshiba’s existing products. This higher rating extends the range of supported equipment and allows for its use in higher-power applications.
Despite the higher ratings, the package is smaller. The TPD4165K comes in a 30-lead through-hole HDIP30 package measuring just 32.8 × 13.5 × 3.525 mm, with a 21% smaller footprint than the DIP26 package used for many of Toshiba’s previous products. The smaller package eases the design process for challenging space-constrained applications.
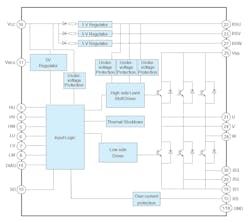
The TPD4165K BLDC motor driver, designed for high-voltage pulse-width-modulation (PWM) control, is fabricated using a high-voltage silicon-on-insulator (SOI) process. It contains a level-shifting high-side driver, low-side driver, IGBT outputs, fast-recovery diodes (FRDs) for efficiency, protective functions for overcurrent and undervoltage protection circuits, and a thermal-shutdown circuit (Fig. 1).
Acknowledging that the power-supply voltage may fluctuate significantly in some regions where this device could be used, the absolute maximum voltage rating (VBB) has been increased to 600 V—a 20% increase over Toshiba’s previous products—thus enhancing long-term reliability. The IC supports either three-shunt or single-shunt resistor circuits for current sensing, and it can be used in sensorless, vector control designs.
An external signal can be applied to the SD pin to control the behavior of the output stage, while an output pin provides the status of the safety conditions. A bootstrap circuit offers a simple high-side supply, and bootstrap diodes are built in.
Design-in Support for the IPD
Most designers don’t have the time, expertise, or desire to design a complete motor-driver subsystem, and vendors are fully aware of this reality. At the same time, designers assume that vendors know their parts and their inherent and unavoidable idiosyncrasies better than a first-time user. Thus, a reference design is a standard companion to the release of an IC in this class.
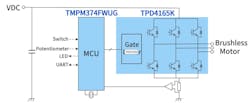
For these and other reasons, Toshiba offers a free reference design for a sensorless BLDC motor-drive circuit based on the TPD4165K and the company’s TMPM374FWUG microcontroller with vector control engine capability (Fig. 2).
This 85- × 130-mm reference design provides a design guide, schematic diagram, bill of materials, and software for a design. It implements sensorless vector control with the MCU designed for motor control, and there’s a removable accessory board with setup and configuration control (Fig. 3).
Key features of the reference design include:
- Motor power-supply input voltage: 120 to 340 V DC
- Maximum motor-drive current: 3 A per phase
- Motor current detection: three shunt or single shunt
- Control power input: 15 and 5 V DC
Full details on the TPD4165K motor IPD device and its reference design, including a short video, are available here.
About the Author

Bill Schweber
Contributing Editor
Bill Schweber is an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times, as well as both the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
At Analog Devices Inc., Bill was in marketing communications (public relations). As a result, he has been on both sides of the technical PR function, presenting company products, stories, and messages to the media and also as the recipient of these.
Prior to the MarCom role at Analog, Bill was associate editor of their respected technical journal and worked in their product marketing and applications engineering groups. Before those roles, he was at Instron Corp., doing hands-on analog- and power-circuit design and systems integration for materials-testing machine controls.
Bill has an MSEE (Univ. of Mass) and BSEE (Columbia Univ.), is a Registered Professional Engineer, and holds an Advanced Class amateur radio license. He has also planned, written, and presented online courses on a variety of engineering topics, including MOSFET basics, ADC selection, and driving LEDs.