Dual High-Side Switches Reliably Drive Non-Resistive Multi-Amp Loads
Despite all of the attention devoted to low voltage, low operating, and quiescent currents, and low power in general, the reality is that many applications require more power during real “work” as defined by physics, which usually means high current levels. Switching this current can be a design challenge, especially when the application involves high-side (non-ground referenced) switching or non-resistive loads such as motors.
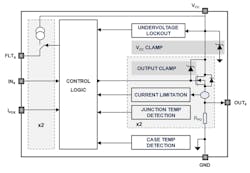
That’s where two new, similar dual high-side switches from STMicroelectronics (ST) can help. The IPS2050H and similar higher-current IPS2050H-32 support two user-programmable current-limit settings for smart driving of capacitive or inductive loads that draw high startup current (Fig. 1). These new dual-channel switches have an input-voltage range from 8 to 60 V and can withstand up to 65 V on the input pin, ensuring flexibility and robust performance in industrial applications, vending machines, PLCs, machine tools, and similar.
The IPS2050H’s main current limit can be programmed up to 2.5 A while the similar IPS2050H-32 has a higher maximum-current limit of 5.7 A for use with unidirectional motors in equipment. The integrated power MOSFET maintains low RDS(on) of below 50 mΩ up to TJ = 125°C, corresponding to 2.4-/5.6-A steady-state operating current.
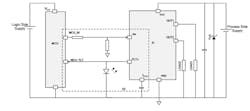
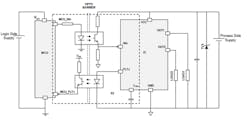
The switches can be used in non-isolated load-driving configurations (Fig. 2) as well as isolated ones (usually via an optocoupler) (Fig. 3). In addition, the single-pulse avalanche-energy rating of greater than one joule at 2 A boosts reliability for handling inductive loads.
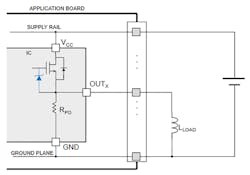
There’s also an active clamp for fast demagnetization (fast current decay) of inductive loads (Fig. 4). When a high-side driver turns off an inductance, an undervoltage is detected on the output and the output pin is pulled down to VCC-VDEMAG. The conduction state is modulated by internal circuitry to keep the output pin voltage at ~VDEMAG until the load energy has been dissipated in both ICs’ internal switch and the load resistance.
The current-activation threshold and limit values are configurable using external resistors. An external capacitor sets the duration of the startup current limit for smart driving of capacitive loads.
Extensive built-in protection features and diagnostics include undervoltage lockout (UVLO) and protection against overvoltage, overload, short-circuit, ground disconnection, and VCC disconnection. Each output channel is independently protected against junction overtemperature events by a junction-temperature sensor. Another temperature sensor monitors case temperature, so an overheated output channel can only be turned back on when the case temperature returns below the reset temperature.
The IC offers two different sets of activation threshold and limitation levels for smart driving of capacitive loads (such as bulb lamps) and loads with initial peak-current requirements.
The 28-page datasheet provides full static and dynamic specifications along with thermal and other timing diagrams. For development support, ST offers demonstration boards and software to ease evaluation of the driving and diagnostic capabilities when connected to industrial loads.
These include the X-NUCLEO-OUT03A1 (Fig. 5) and X-NUCLEO-OUT04A1 digital-output expansion boards for the IPS2050H and IPS2050H-32, respectively, for use with available development boards, along with the various associated software drivers. In addition, graphical-user-interface (GUI) source code enables users to operate in an entire industrial automation environment.
The switches meet IEC 61000-4-2 ESD, IEC 61000-4-4, and IEC 61000-4-5 specifications for ESD, fast-transient, and surge immunity. Both switch versions come in a compact, space-efficient PowerSSO-24 package and are priced beginning at $3.19 (1,000 pieces).