Battery-Cell Charging Basics (Download)
Charging and discharging are the most fundamental actions applied to cells by cell researchers, cell manufacturing engineers, and battery-pack designers. In this article, I will cover the basics of how a cell charger/discharger functions. I also will touch on how contacting the cell through its fixture is an important part of successful charging and discharging.
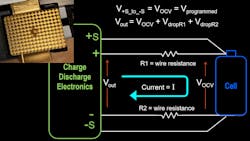
Typically, a lithium-ion cell is charged using a constant-current/constant-voltage (CC/CV) charging step. During discharge, a constant-current (CC) discharge step is most often used. How does a charger achieve CC/CV, or a discharger achieve CC?
If we look at basic electronics, a charger is a power supply, very similar in design to any simple benchtop power supply you have encountered in an electronics lab. A power supply allows the user to set a voltage operating point, which is sometimes called the voltage limit or constant-voltage (CV) setpoint. If the power supply is a CV/CC-type supply, then the user also can set the current limit or CC setpoint.