Power Efficiency and Adaptable Performance: The Enduring Legacy of 8-Bit MCUs
What you’ll learn:
- Core independent peripherals (CIPs) on 8-bit MCUs are pivotal in designing low-power solutions for various applications, including sensor nodes and real-time control systems.
- Multi-voltage I/O enables a single MCU port to operate in a different voltage domain than the rest of the MCU.
- Integrated op amps, along with analog-to-digital converters with computation featuring built-in computational functions such as oversampling, averaging and low-pass filtering, enhance signal-processing capabilities.
- Modern 8-bit MCUs often provide power efficiency and a better balance of peripheral features compared to similarly priced 32-bit devices, enabling them to manage more tasks in hardware and extend CPU sleep-mode times.
The 8-bit microcontroller (MCU) has been a staple in the world of embedded design for over half a century. Despite the complexity that has developed in the embedded systems market, the 8-bit MCU continues to evolve, adapting to new challenges and system requirements.
Today, many microcontrollers are equipped with advanced core independent peripherals (CIPs) and intelligent analog peripherals. These innovations enhance the capabilities of control systems, reduce power consumption, and speed up both development and market entry.
Core Independent Peripherals: A New Standard
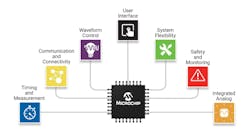
CIPs are specialized hardware components that function independently from the central processing unit (CPU) (see figure). These peripherals on 8-bit MCUs are pivotal in designing low-power solutions for various applications, including sensor nodes and real-time control systems. By offloading tasks from the CPU, CIPs help lower overall power consumption while ensuring reliable, deterministic responses.
More 8-bit Micro Articles
The reduction in code size and the time saved during development, coupled with the increase in available memory space for applications, are significant advantages. Development tools like the MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC) can further simplify the development process, making it more accessible for a wide array of developers in the embedded systems community.
Highlighted CIPs that Enhance Efficiency
- Multi-voltage I/O (MVIO): MVIO enables a single MCU port to operate in a different voltage domain than the rest of the MCU, eliminating the need for external components when interfacing devices with different supply voltages, such as connecting a 5-V MCU to a 1.8-V sensor.
- I3C communication: The introduction of I3C in microcontrollers meets the growing demand for higher data rates in applications like cloud-connected edge nodes and sensor interfaces requiring high-speed, low-power communication.
- Configurable logic block (CLB): The CLB is a reconfigurable digital logic module integrated into the MCU, akin to a complex programmable logic device (CPLD). It consists of 32 logic elements based on a lookup table (LUT) design, enabling engineers to create custom hardware-based logic functions within the microcontroller.
Intelligent Analog Peripherals
Microcontrollers equipped with intelligent analog peripherals play a crucial role in functions ranging from system management to complex controller duties. By bringing tasks typically handled off-chip onto the main MCU, these peripherals improve system response and reduce bill of materials (BOM) costs. These analog peripherals automate signal analysis, provide compensation data for digital pulse-width modulators (PWMs), and offer auto-shutdown capabilities without requiring CPU intervention.
Key Analog Peripherals
- Operational amplifiers (op amps): The integration of op amps as peripherals allows for the creation of analog circuits within the MCU, potentially reducing the need for external components.
- Analog-to-digital converter with computation (ADCC): The ADCC is an advanced peripheral that features built-in computational functions such as oversampling, averaging, and low-pass filtering, enhancing signal-processing capabilities.
Streamlining Development with Ease of Use
One of the most effective ways to shorten software development time is to reduce the amount of code required. Both 8-bit PIC and AVR microcontrollers are designed for efficient use of their peripherals, minimizing the lines of code needed for common functions. This efficiency accelerates the development process, as the hardware's functionality is factory-validated, simplifying coding and ensuring reliability.
Balancing Power and Performance
Power consumption remains a critical consideration in embedded systems design, especially in applications like wireless sensors, automotive systems, household appliances, and medical devices. Although 32-bit MCUs are faster, they typically consume more power. The lower power consumption of 8-bit MCUs, particularly in run mode, ensures longer battery life and makes them an ideal choice for many applications.
In addition, modern 8-bit MCUs often provide a better balance of peripheral features compared to similarly priced 32-bit devices, enabling them to manage more tasks in hardware and extend CPU sleep-mode times. For certain applications, the CPU uptime requirement is nearly zero, giving 8-bit MCUs a distinct advantage.
8-Bit is Here to Stay
Despite advances in technology, 8-bit microcontrollers remain essential due to their efficiency, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness. Modern devices, like Microchip’s PIC and AVR MCUs, offer advanced CIPs and intelligent analog features that automate signal processing and optimize power management, suiting them for energy-sensitive applications like wireless sensors and automotive systems. The flexibility of features such as multi-voltage I/O and configurable logic blocks facilitates the creation of complex, custom solutions and reduces the need for external components.
As embedded systems continue to evolve, the unique blend of performance, power efficiency, and development simplicity offered by 8-bit MCUs ensures their lasting importance. Whether it’s extending battery life or integrating smart peripherals, 8-bit microcontrollers will continue to play a crucial role in modern embedded design. The bottom line is that there will always be a place in the embedded market for cost-effective, energy-efficient 8-bit MCUs.
About the Author

Ulises Iniguez
Marketing Engineer, Microchip Technology
Ulises Iniguez is a Marketing Engineer at Microchip Technology with more than three years of experience specializing in entry-level microcontrollers. He creates technical content, including articles and YouTube videos, to help embedded engineers on their design journey. At industry conferences, he supports hands-on demos that showcase innovative applications of embedded technology. Ulises holds a BS in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Notre Dame.